Climate, Environment, and Social

Decarbonization and Climate Strategy
Our vision of Renewable Energy Leadership is based on a comprehensive approach grounded in scientific evidence, policy advancements, and technological transformation. Within this framework, our decarbonization and net-zero strategy aims not only to follow Türkiye’s national energy transition but to emerge as a leading force shaping that transformation.
Decarbonization stands as a top strategic priority. Key objectives include investing in low-carbon technologies, expanding green electrification, and supporting Türkiye’s 2053 net-zero target. While driving the energy transition, we identify our climate-related impacts, dependencies, risks, and opportunities in alignment with international standards, integrating climate adaptation and mitigation strategies into all business processes. This strategic framework prioritizes renewable, hybrid, and storage solutions to enhance the flexibility of our energy system and strengthen our digital capabilities.

Our Commitment to the Decarbonization Journey: Net Zero Carbon by 2040
Enerjisa Üretim’s climate transition framework has been updated in line with current scientific data and policy expectations. As part of this update, the reference scenario in its long-term decarbonization roadmap has been revised, moving the target year from 2045 to 2040. This new target aligns closely with several key benchmarks, including the 1.5°C-aligned C2 scenarios outlined in the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6)1, the International Energy Agency’s Net Zero by 2050 roadmap, and the European Union’s 2040 goal of a 90% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, it is structurally consistent with Türkiye’s 2053 net-zero vision and the 2035 renewable energy capacity projections set out in the Türkiye National Energy Plan (TUEP).
The net-zero carbon scenario for 2040 is framed as a probabilistic pathway, shaped by current technological, economic, and regulatory conditions. Its feasibility will depend on a range of dynamic factors, including policy developments, access to finance, system flexibility, technology maturity, and operational transformation capacity. Within this context, the analyses and roadmap presented in the Climate Transition Plan offer a probability-based transformation model built on defined assumptions.
Updating the scenario marks a strategic milestone, particularly in areas such as low- carbon transformation of the generation portfolio, acceleration of renewable energy investments, development of flexible thermal infrastructure, and expansion of energy storage solutions. The emissions reduction targets extend beyond operational activities, encompassing all corporate decision-making mechanisms—from governance to investment planning.
Built on this strategic direction, the Climate Transition Plan outlines the 2030 emissions intensity target in alignment with the IPCC C2 – 1.5°C scenario with high overshoot, along with the corresponding short-, medium-, and long-term strategic actions. The plan adopts an analysis-based approach to assess both resilience to climate-related risks and preparedness for emerging opportunities.
The table below presents our updated emission intensity projections.
Our Strategic Pillars
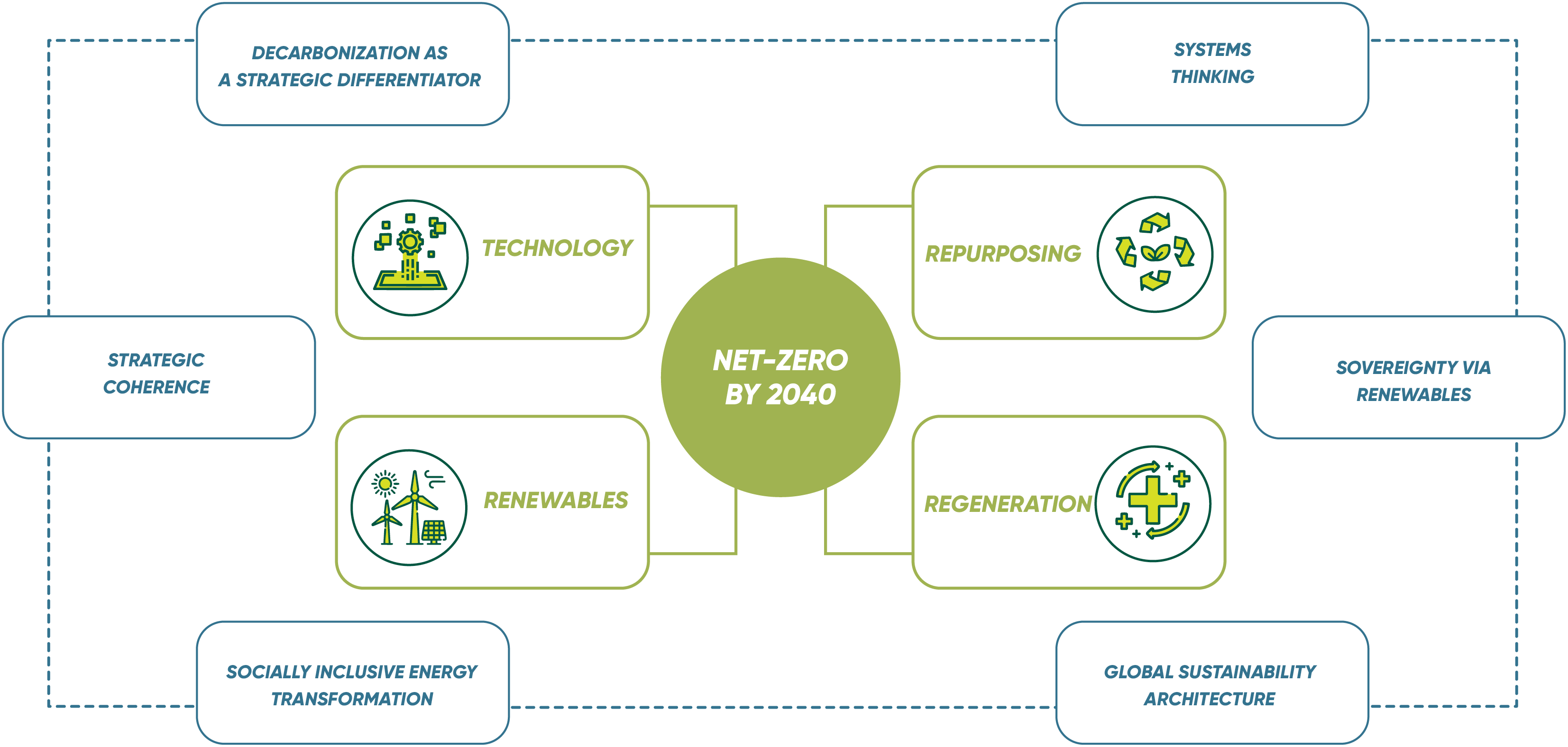
Enerjisa Üretim’s climate strategy is shaped by a holistic assessment of scientific data, policy developments, technology trends, and societal expectations. Six core principles form the corporate foundation of this strategic direction:
Six fundamental principles form the institutional basis of this strategic orientation:
- Decarbonization as a Strategic Differentiator
- Carbon Pricing and Regulation as Enablers of Strategic Coherence
- System Thinking in Power Sector Innovation
- Energy Security Through Renewable Sovereignty
- Engagement with the Globally Sustainability Architecture
- Just and Regenerative Transition
These principles not only enhance corporate resilience against climate risks but also enable us to approach the energy transition as a sustainable value creation process.
For detailed explanations and implementation steps of these principles, please refer to our Climate Transition Plan.
Focus Areas on Our Net Zero Journey
Our climate transition strategy is supported by four main focus areas that address the transformation comprehensively, not limited to reducing carbon emissions but encompassing technological, ecological, and systemic dimensions.
1. Increasing Renewable Energy Capacity
| Capacity Expansion in Existing Assets Incremental capacity upgrades at operational plants enhance production efficiency while optimising the use of existing infrastructure and permits. These investments enable increased output without the need for additional greenfield developments. |
| Development of New Projects through the YEKA Mechanism Wind auctions conducted under Türkiye’s YEKA model form the foundation of the company’s large-scale renewable energy investments. As a result of the YEKA- 2 wind power auctions, pre-license rights totaling 1,000 MW were secured in Aydın, Çanakkale, Balıkesir, and Muğla. In 2024, an additional 750 MW of capacity was allocated through the Edirne and Balkaya projects. Once completed, these investments are expected to prevent approximately 3.6 million tons of CO2 emissions annually. |
| Portfolio Expansion through Mergers and Acquisitions The renewable asset portfolio is being strengthened through mergers and acquisitions. In addition to the Akhisar, Çeşme, Dikili, and Aydos wind farms, the pre- license for the Karaburun wind power project has also been incorporated into the portfolio. Acquisitions are made with careful consideration of asset quality, ease of grid connection, and hybrid/repowering potential. |
| Hybrid Power Plant Integration Hybrid power plants combining wind and solar integration play a crucial role in demand-side flexibility and on-site emission reduction. A total of 90.69 MW of hybrid solar capacity has been commissioned, with a target of reaching 150 MW by 2027. |
| Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) Battery systems are being deployed in integration with renewable assets. Enerjisa Üretim has secured a preliminary license for 500 MWh of storage capacity, and a pilot project with a 2 MW / 4 MWh capacity has been commissioned at the Bandırma Energy Hub. These systems hold strategic importance for maintaining grid frequency stability, reducing interruptions in renewable generation, and limiting the need for fossil fuel backup capacity. |
2. Technological Innovation and Operational Optimization
We are implementing technological solutions to reducethe emissions intensity of our existing assets. The Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) pilot project targets the separation of both CO2 and other pollutants from flue gases to produce fertilizer, contributing to the circular economy. Through AI-driven systems, battery integrations, and the electrification of mining operations, we are enhancing operational efficiency and developing solutions to address residual emissions.
3. Controlled Reduction of Fossil Based Generation
Without decommissioning our thermal power plants, we are restructuring them to serve as flexible backup capacity and transitioning to a model that continuously manages carbon intensity. . Hybrid solutions, fuel flexibility, and low-capacity factor operating principles are being implemented at the Bandırma and Tufanbeyli Energy Hubs. This approach preserves supply security while minimizing emissions.

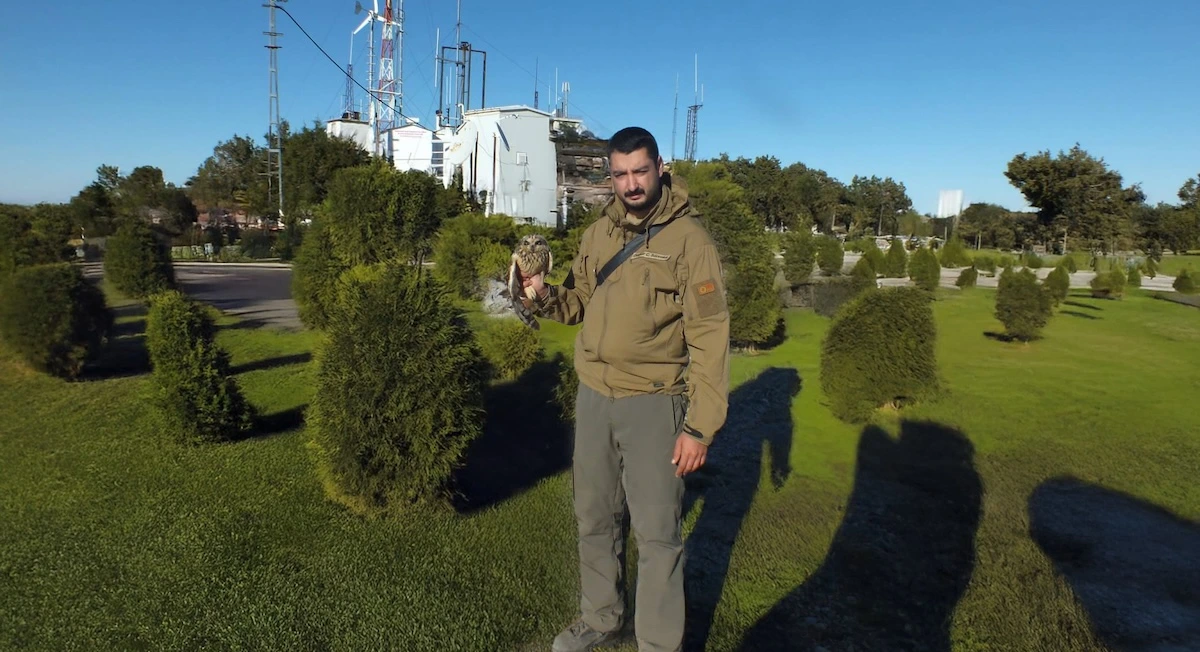
4. Nature-Based Solutions and Ecosystem Restoration
Enerjisa Üretim views its climate strategy as more than just technical reductions, complementing it with nature-based solutions. Through afforestation, agrivoltaic applications, biodiversity management, and sustainable water use projects, we strengthen carbon sinks, enhance ecosystem resilience, and support local adaptability. Through our collaborations with the General Directorate of Forestry (OGM) and General Directorate of Forestry Education and Culture Foundation (OGEMVAK),we stand as the leading private sector actor in Türkiye in terms of the number of saplings planted. As part of these efforts, we aim to plant around 7 million trees by 2040. Our agrivoltaic projects at the Bandırma and Komşuköy sites improve agricultural yields and protect soil moisture; meanwhile, the irrigation transformation project in the Sarıgüzel basin saves 1.3 million m2 of water annually and reduces CO2 emissions by 280 tons. These initiatives represent tangible components of a nature- positive transition.
Our commitment to net zero carbon by 2040
Approximately 60% renewable portfolio with 7,500 MW installed capacity by 2030
Representation of at least 10% of Türkiye’s wind energy capacity
As of 2027, the leading private sector company in Türkiye for tree planting, targeting 2 million saplings
Preventing at least 4.5 million tons of carbon emissions annually through wind energy investments 14
[14] As of 2027
Our climate strategy is built on innovative solutions and sustainable energy technologies that support low- carbon growth. We manage climate risks, seize opportunities, and lead the transformation to create a better future and a resilient business strategy.
Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities
Climate risks and opportunities have been assessed within the framework of various international climate scenarios. These scenarios include outcomes ranging from limiting temperature rise to below 2C to increases of up to 3.5-4C. The analyses have been conducted in alignment with TCFD recommendations. This approach enables a deeper understanding of potential climate impacts, supporting informed strategic.
Asset-Based Evaluation
All our generation assets have been thoroughlyexamined in terms of their carbon intensity, integration of hybrid capacity, contributions to renewable energy, and impacts on grid flexibility.
Stakeholder-Driven Governance
Internal working groups, cross-departmental task forces, and the Sustainability Steering Committee guide scenario prioritization, while dialogues with external consultants, industry experts, and investors have shaped the contextual framework and priority analyses.
Policy Compliance and Agility
The plan emphasizes its alignment and adaptabilityto evolving regulations, taking into account the Turkish National Energy Plan, emerging ETS frameworks, the EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM),and decisions made at COP28.

Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities
Enerjisa Üretim has reviewed all climate scenarios outlined by these authorities and integrated them with its own forecasts and projections to establish two scenarios: the “ambitious climate transition” scenario, which anticipates global warming remaining well below 2ºC by the end of the century, and the “slow climate transition” scenario, which projects global warming between 3.5 and 4ºC.
| Scenario Sources | Ambitious Climate Transition | Slow Climate Transition |
|---|---|---|
| IPCC 15 | SSP1-2.6 (Radiative Forcing, similar to RCP) | SSP3-7.0 |
| RCP | RCP2.6; RCP4.5 (Only associated with SSP1) | RCP6.0; RCP 8.5 (Not associated with the highest SSP) |
| SSP | SSP1* SSP2 | SSP3; SSP4; SSP5 (SSP 5 linked only with low RCPs) |
| IEA | NZE** | STEPS (Associated with "high" SSP) |
| NGFS | Below 2 ºC | Current policies |
Assessment of Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities and Risk Mitigation
Enerjisa Uretim’s Climate-Related Risks
We categorize climate-related risks into two main groups:
- Transition risks, which arise from actions such as the implementation of new climate policies and the adoption of low- carbon technologies during the shift to a low-carbon economy.
- Physical risks, which stem from both acute and long-term physical impacts of climate change, resulting in acute and chronic effects on the environment and ecosystems.
We assessed our transition and physical risks under various warming scenarios, Ambitious Climate Transition (< 20C) and Slow Climate Transition (3.5-40C),by analysing their impacts across every part of our value chain (supplier phase, direct operations, and customer side) and identified our priority climate risks.
Enerjisa Üretim’s key climate-related risks include:
- Drought / water stress
- Carbon pricing / accelerated carbon reduction
- Potential disruptions in raw material supply chains
| Physical(P) Transition (T) | RISK CATEGORY | RISK CATEGORY | Risk Score | Applicability to Value Chain | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2° C Scenario | 3,5–4° C Scenario | Upstream | Direct Operations | Downstream | |||
| F | Chronic physical | Drought/water stress | X | X | X | ||
| G | Policy and Regulatory | Carbon pricing/Accelerated decarbonization | X | X | X | ||
| G | Market | ÜChanging counterparty behavior | X | X | X | ||
| G | Market | Disruptions in the raw materials supply chain | X | X | X | ||
| G | Reputation | Rise in public activism and litigations | X | ||||
| F | Chronic Physical | Changing wind patterns | X | X | X | ||
| G | Market | Decentralization of the grid/Changing commodity market/price dynamics | X | X | X | ||
| F | Acute physical | Wildfire | X | X | X | ||
| F | Acute physical | Hailstorms | X | X | X | ||
| F | Acute physical | Flood | X | X | X | ||
| F | Acute physical | Landslide | X | X | X | ||
| G | Policy and Regulatory | Enhanced reporting obligation | X | ||||
| G | Technology | New technologies in the energy generation sector | X | X | |||
| F | Chronic Physical | Rise in mean temperatures | X | X | X | ||
| F | Acute physical | Severe changes in temperatures | X | X | X | ||
Hight Medium High Medium Low Low | |||||||
Climate Related Opportunities for Enerjisa Üretim
Thanks to lts position in the energy market and diverstied portfolio, Enerjisa Oretim has idensified a range of promising dimate related opportunities within Turklye’s transition to cleaner energy, especially under the Ambitious Climate Transition scenario ( < 2°C).
| Opportunity Category | Opportunity Category | Opportunity Score | Applicability to Value Chain | Description of Opportunities | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2°C Scenario | 3.5–4°C Scenario | Upstream | Direct Operations | Downstream | |||
| Energy Source | Use of policy incentives | X | X | X | In the <2°C scenario, investments and policy incentives aimed at expanding renewable energy capacity are notably strong. However, such structural advancements are unlikely to materialize in a 3.5–4°C world. Turkey’s National Energy Plan anticipates an increase in renewable energy use; nevertheless, this growth does not reach the levels projected under an ideal <2°C scenario. These projections rely on existing incentives, and the energy sector remains highly sensitive to these dynamics. | ||
| Resilience | Expansion of and increased participation in carbon markets | X | X | Opportunities exist in the issuance and sale of energy attribute certificates (EACs),including carbon credits and renewable energy certificates (RECs),within both voluntary and potentially mandatory markets. Carbon pricing is more probable under the <2°C scenario, with higher expected prices. Increased participation in Turkey’s voluntary carbon market (VCM) alongside the implementation of a national Emissions Trading System (ETS) could present significant revenue opportunities through carbon credit sales. | |||
| Energy Source | Use of lower-emission sources of energy / technologies | X | X | X | There are also opportunities stemming from the expansion of low- or zero-emission power generation capacity. Under the <2°C scenario, the share of renewables in the global primary energy mix is expected to be substantially higher compared to a 3.5–4°C scenario. Turkey’s renewable energy efforts continue steadily, with Enerjisa Üretim’s portfolio already well diversified in line with these trends. | ||
| Markets | Positive investor sentiment towards renewables | X | X | Leveraging positive investor interest in renewables, sustainable financing instruments such as green bonds and sustainability-linked loans offer project financing opportunities. Consumer awareness is greater in the <2°C scenario, which further boosts investor interest compared to the 3.5–4°C scenario. Turkey is expected to align with these global awareness trends. | |||
| Energy Source | New technologies | X | X | X | Development and investment in new clean energy technologies also represent significant opportunities. Battery storage and carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies are anticipated to advance considerably under the <2°C scenario, while hydrogen technologies are projected to be more prominent in the 3.5–4°C scenario. Approximately 40% of Enerjisa Üretim’s portfolio is dedicated to renewables, and coupling this base with advanced storage technologies holds substantial potential. | ||
| Products and Services | Increased use of corporate power purchase agreements (PPAs) | X | Corporate Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) driven by emission reduction and Net Zero targets present major opportunities. While the scale of PPAs may vary across climate scenarios, their rapid adoption in Turkey, especially within the energy sector, is expected to continue. | ||||
| Resilience | Improving resilience with advanced and emerging technologies | X | Using advanced and emerging technologies to enhance maintenance operations and ensure production continuity also creates opportunities. Adoption rates for technologies like photovoltaic (PV) systems are likely similar in both scenarios, though usage is expected to be more widespread under the <2°C scenario. Turkey is clearly exposed to this trend, and Enerjisa Üretim is already exploring these technologies. | ||||
| Energy Source | Rising in average temperatures | X | Rising global temperatures could significantly increase cooling demand, which is expected to have notable effects in Turkey. This increase in demand will occur regardless of the energy portfolio composition. | ||||
| Products and Services | Increased industrial and/or household use of micro-generation / Decentralization of the grid | X | X | The growing use of micro-generation technologies, such as rooftop solar panels in industry and households, presents additional opportunities. This trend applies across both scenarios but is expected to have a greater impact in the <2°C scenario, where battery technology is more advanced. Although Turkey’s grid does not yet have smart infrastructure, there is considerable potential for growth in battery storage technology within industrial and residential sectors. | |||
High Medium High Medium Low Low | |||||||
Carbon Management
Our greenhouse gas emissions stemming from our operations are rigorously tracked through an advanced monitoring and reporting system designed to fully understand and manage our company’s environmental impact. This system classifies all emissions from operational processes into three main categories in accordance with the GHG Protocol: direct emissions (Scope 1),indirect emissions from purchased energy (Scope 2),and indirect emissions across the value chain (Scope 3). Data for each emission source is meticulously calculated and monitored on an annual basis, enabling continuous improvement and optimization. At our thermal power plants, emissions are verified annually through comprehensive, site-based production-related emission audits in compliance with the Monitoring Greenhouse Gas Emissions Regulation.
As of 2023, we expanded the calculation of our Scope 3 emissions from 5 subcategories to 9 by covering our entire value chain, and subjected them to limited assurance for the first time. This milestone significantly strengthened our level of corporate transparency and accountability in managing indirect emissions. When considered alongside Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, our Scope 3 emissions enable a holistic management of Enerjisa Üretim’s climate impact throughout the entire value chain. Structured under nine priority categories, this analysis not only expands the scope of our emissions inventory but also identifies high-impact sources, allowing us to base our reduction strategies on a more targeted and effective foundation.
KDetailed examination of data from various sources such as supply chain, capital investments, transportation, waste, business travel, and product use has transformed Scope 3 emissions from a mere tracked metric into an active management tool fully integrated into our strategic planning processes.
Environmental Management
All our operational and new investment processes are designed in full compliance with both national and international environmental regulations, fulfilling our environmental responsibilities and reflecting our commitment to future generations. In this context, prioritizing the implementation of necessary measures to minimize environmental impacts, meeting the expectations of national and international stakeholders, and continuously monitoring compliance with relevant obligations are fundamental to our approach. We continuously enhance our environmental management practices by working closely with local and international regulatory authorities, aiming to develop innovative strategies that reduce negative environmental effects. All necessary permits and approvals have been secured to ensure rigorous monitoring and regular reporting of the environmental impacts of our operations.
Environmentally conscious and sustainable practices are prioritized throughout our all processes. Environmental impacts are consistently monitored at every stage of production, with improvement measures implemented as needed. Under our environmental management system and in accordance with the ISO 14001:2015 standard, we conduct environmental audits and internal inspections across all activities. Comprehensive external audits conducted in 2024 identified no non-compliances, confirming full adherence to legal requirements and corporate standards. Throughout the year, no environmental incidents occurred across any field operations; emergency response plans, regular site inspections, and training programs have supported a proactive approach to potential risks.
At Enerjisa Üretim, we conduct comprehensive efforts across all project sites where our new investments are underway to minimize environmental impacts and ensure effective waste and emissions management. We systematically monitor the activities of our subcontractors in compliance with the International Finance Corporation (IFC) standards, maintaining regular records on water, wastewater, noise, air quality, soil, noise, waste, and chemical management. Through emission measurements at generators, dust control via irrigation and monitoring, use of energy-efficient equipment, waste and wastewater management, and environmental awareness training, we not only ensure environmental compliance but also continuously improve our operational processes.
To effectively manage environmental impacts in our projects and power plants, we implement extensive environmental management procedures aligned with the environmental performance standards of international finance institutions such as IFC and EBRD. Within this framework, water and wastewater management incorporate recovery and reuse methods, while air quality is safeguarded through dust suppression and emission control measures. Chemicals used on site are managed under secure storage and handling protocols; soil excavated during construction is stored separately for rehabilitation purposes, and erosion risks are actively mitigated. Hazardous and non-hazardous waste is segregated and managed through recycling, recovery, or appropriate disposal methods. Groundwater and surface water are regularly monitored, and drainage systems are implemented to protect water resources. All these activities are carried out in full compliance with IFC PS6, EBRD PR6, GRI 304, and EU environmental legislation, aiming to conserve and enhance biodiversity.
Throughout the year, all our plants have undergone extensive audits conducted by various public authorities and financial institutions. Each of these audits was successfully completed without any non- compliance issues or findings. During the inspections, our environmental management systems and operational processes were thoroughly reviewed, confirming full compliance with applicable all environmental regulations, sustainability principles, and corporate standards. This positive outcome reflects our environmental management policies that proactively identify and effectively mitigate environmental risks, supported by our ongoing commitment to continuous improvement. We have enhanced operational efficiency and maintained all our activities in accordance with international environmental standards.
Our efforts in environmental management are made possible by our employees’ strong environmental awareness and dedication to corporate compliance. In line with our philosophy of continuous improvement, we will continue to implement innovative practices and steadfastly pursue sustainability-driven strategies to further advance our environmental performance.
Water and Waste Management
Water Management
At Enerjisa Üretim, we conduct risk assessments and detailed water analyses to ensure the sustainable use of water resources and to minimize water stress risks. Given Türkiye’s status as a water- stressed country, we develop water conservation strategies across all our operations. At our thermoelectric power plants, which have a high dependence on water, we continuously improve processes to reduce water withdrawal and increase water recovery. For every facility where water is withdrawn, the characteristics of the receiving water body are carefully considered, with specific standards applied for different sources such as seas, rivers, and lakes. While complying with local regulatory requirements for water withdrawal, we continually enhance our water management practices in line with international standards.
| Parameter | 2024 | 2023 | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Volume of Water Withdrawn | 307.606.305 | 335.749.185 | -8% |
| Fresh Water | 2.698.295 | 2.779.319 | -3% |
| Sea Water | 304.900.915 | 332.962.917 | -8% |
| Other | 7.095 | 6.948 | 2% |
| Total Volume of Water Discharged | 304.741.579 | 332.793.313 | -8% |
| Fresh Water | 112.098 | 104.750 | 7% |
| Sea Water | 304.621.765 | 332.679.304 | -8% |
| Other | 7.716 | 9.259 | -17% |
| Volume of Water Recovered | 816.569 | 863.027 | -5% |
Throughout our construction activities, water supply and distribution operations conducted by our subcontractors continuously monitored through detailed analyses. Water usage on construction sites has been recorded to ensure efficient use and to implement effective measures for water resource conservation. Additionally, potential losses and leaks during water supply processes have been promptly identified and addressed through regular inspections.
Within the Environmental and Social Impact Assessment (ESIA) processes for our projects, groundwater wells sampled during construction phases have been regularly tested to detect any potential contamination, tracking water quality changes over time. Upon project completion, follow- up analyses have been conducted to evaluate final conditions, and results have been documented. This process ensures the protection and sustainable management of groundwater resources in the long term.
Standardized methodologies and verified data sources form the basis for determining water withdrawal volumes. These approaches are detailed as follows:
- For facilities equipped with meters, water withdrawal is calculated based on meter readings.
- For transport water purchased from third parties, calculations are made according to vehicle capacity.
- Consumption of water supplied from municipal networks is monitored through invoiced amounts.
- For bottled water, the quantities stated on invoices are considered.
Wastewater Management
Wastewater management is executed in compliance with national and international standards, aimed at mitigating environmental impacts and enhancing our sustainability performance. Priority substances and control parameters for wastewater treatment are defined based on legal requirements, international standards, and internal company criteria.
Our wastewater discharge management adheres to the Water Pollution Control Regulation (SKKY) and relevant international standards, implementing a comprehensive discharge management system. Local and international requirements are strictly followed to protect water resources, with additional criteria applied in line with IFC Performance Standards and EBRD Performance Requirements. Internal standards aligned with financial institutions’ sustainability criteria and our own environmental commitments have also been established. Regular analyses are conducted at sites with wastewater treatment facilities, ensuring monitored parameters remain within designated limits.
Because receiving environments (seas, rivers, lakes, etc.) differ in characteristics, discharge limits are established considering regional environmental conditions. Water quality parameters and discharge limits are continually monitored and analyzed, with ongoing process reviews to mitigate environmental impacts.
Key parameters prioritized in wastewater treatment include temperature, chemical oxygen demand (COD),suspended solids (SS),biochemical oxygen demand (BOD),pH, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, total coliform, oil, and grease. To date, no non-compliance has been identified.
Domestic wastewater generated at subcontractors’ mobilization areas is securely stored in sealed septic tanks to prevent environmental contamination. Waste accumulated in these tanks is regularly removed and transported to municipal wastewater treatment plants.
We have initiated compliance efforts with the European Union (EU) Taxonomy and the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD).
Our compliance efforts with the European Union’s (EU) Taxonomy, which sets sustainability criteria, and the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD),which establishes the framework for protecting water resources, represent a significant milestone in advancing our environmental and operational sustainability objectives. These initiatives aim to ensure full alignment of our operations with international sustainability standards and environmental management requirements.
As part of the EU Taxonomy compliance process, we conduct detailed analyses of the environmental impacts of our operations, evaluating performance indicators across critical areas such as energy efficiency, carbon reduction, circular economy, and climate change mitigation. Meanwhile, our alignment with the EU Water Framework Directive focuses on the effective and efficient management of water resources. In this context, we implement projects to enhance water use efficiency and carry out measures to protect and improve water quality. Sustainable practices are actively adopted across our operational sites to reduce water consumption, improve wastewater management, and safeguard water resources.
Sarıgüzel Agricultural Irrigation Infrastructure Project
Located downstream of the Sarıgüzel Hydroelectric Power Plant, the Sarıgüzel Irrigation Project exemplifies a science- based approach to sustainable water resource management and ecological resilience. Developed through detailed hydrological modelling, the project replaces the traditional open channel “wild irrigation” method on 23 hectares of farmland with pressurized, efficient irrigation systems. These systems incorporate irrigation technologies such as drip and sprinkler irrigation, designed to meet crop water requirements based on climate, soil composition, and crop-specific evapotranspiration data.
The project delivers multiple environmental and socio-economic benefits. It achieves an annual water saving of approximately 1.3 million cubic meters, equivalent to the yearly water consumption of 8,000 people. Main irrigation pipelines have been installed to ensure adequate water delivery, and over 100 farmers have been supported in transitioning to drip irrigation systems, promoting sustainable agricultural practices. Additionally, the project has contributed to an annual reduction of 280 tons of CO₂ emissions. Environmental benefits include preventing soil erosion, enhancing soil retention, and reducing chemical inputs in agriculture by up to 50%, thereby supporting ecosystem balance and increasing agricultural productivity. While strengthening local communities’ resilience to climate change, the project is actively being planned for expansion to cover larger agricultural areas.
Waste Management
To minimize the environmental impact of waste generated through energy generation activities, Enerjisa Üretim implements a comprehensive and integrated waste management system. This system is carried out in alignment with the current Waste Management Regulation and the internal Enerjisa Üretim Waste Management Procedure, with a focus on full regulatory compliance, traceability, and continuous improvement across all processes.
To ensure the effective management of waste, an inevitable byproduct of our production operations, we provide regular environmental awareness and waste management training to both our employees and subcontractors. Process enhancements are implemented to reduce waste generated during maintenance operations, and technical optimizations during equipment replacement and renewal cycles help further minimize waste at the source.
At our facilities, both hazardous and non- hazardous waste is sorted according to type and sent to authorized disposal or recovery facilities via licensed transporters, in full compliance with applicable regulations. All processes are monitored online through MoTAT (Mobile Hazardous Waste Tracking System). For construction- related activities, subcontractor-prepared waste management plans are activated, and temporary waste storage areas with appropriate physical conditions are established at mobilization sites to ensure safe waste handling.
In our waste management approach, we adhere to the following waste hierarchy, in full alignment with both European Union directives and Türkiye’s national regulations:
In line with this hierarchy, a policy is implemented that prioritizes preventing waste generation at its source, promoting recycling, and enhancing opportunities for energy recovery.
| Parameter | 2024 | 2023 | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Waste Amount (tonnes) | 1.478.752 | 2.332.790 | -%37 |
| Non-hazardous Waste (excluding ash waste) (tonnes) | 365 | 1.871 | -%80 |
| Amount of Ash Waste (tonnes) | 1.478.043 | 2.328.801 | -%37 |
| Hazardous Waste (tonnes) | 344 | 2.119 | -%84 |
| Plastic Waste (tonnes) | 17 | 16 | %6 |
In 2024, there was a significant improvement in waste management performance, with a 37% reduction in total waste generated. This decline is largely attributed to the effective management of ash waste and process optimizations. Non-hazardous waste (excluding ash) decreased by 80%, while hazardous waste was reduced by 84%, marking a substantial advancement in mitigating environmental risks. Industry-wide research is ongoing to develop sustainable management strategies for high-volume waste types such as ash; these efforts include exploring alternative uses, recycling methods, and industrial symbiosis opportunities, which are key focus areas for 2025.
As of 2024, 22 power generation facilities along with our Ataşehir headquarters have been awarded the “Zero Waste Certificate.” Additionally, we plan to submit zero waste certification applications in 2025 to the Ministry of Environment, Urbanization, and Climate Change for seven newly commissioned or acquired plants that have completed the project process. This initiative goes beyond regulatory compliance and reflects our commitment to embedding sustainability as a corporate priority across the company.
Circular Economy
One of the core pillars of our waste management strategy is embedding circular economy principles at the heart of our operational processes. In this context:
- The proportion of circular content in procured materials is being increased,
- Waste generated through operations is being reduced,
- Recovery and reuse practices are being promoted,
- Circular collaboration mechanisms are being established across our value chain.
Through this approach, we not only reduce our carbon footprint but also enhance resource efficiency— supporting long-term operational sustainability. The European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) mandate the monitoring and disclosure of circular performance, particularly under E5 – Resource Use and Circular Economy. In line with these regulations, companies are expected to transparently report their resource usage, waste generation, product life cycles, and recovery processes.
Enerjisa Üretim is not only aligning with these requirements but is also restructuring its operations to prepare for additional circularity-focused regulations such as the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) and the European Critical Raw Materials Act.
Adopting circular practices across the supply chain strengthens operational resilience against geopolitical risks, raw material price volatility, and energy crises— while also improving supply security by reducing external dependencies. In this direction, our circular transition strategy has been structured using the Circular Transition Indicators (CTI) methodology and is tied to the following targets:
- Short-term goals (by 2025): Increasing the rate of circular material use and reducing the volume of operational waste,
- Medium-term goals (by 2030): Enhancing recovery and regeneration capacity while minimizing waste disposal rates,
- Long-term goals (by 2050): Improving circular performance in full integration with the supply chain and achieving the Net Zero Waste goal.
As part of this approach, the transition from a linear economy to a circular economy is being accelerated, shifting from the traditional “Buy-Use-Throw Away” model to a more sustainable “Buy-Reuse-Recycle” model. The goal is to utilize resources more efficiently and with lower environmental impact in every production cycle.
General Overview of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Identified for Each Business Unit Based on Three Circular Principles
| Enerjisa Üretim Business Units | Circular Input KPIs | Circular Design KPIs | Circular Output KPIs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Power Plants | % of circular inputs used in wind power plants (investment and repair) Process: Number of components reviewed for technical requirements | % of wind assets procured in line with circular design principles Process: Number of supplier consultations held regarding circular design for wind assets | % of wind turbines included in the circular decommissioning plan % of wind assets recovered Process: Number of reviews conducted on the circular impact of refurbishment |
| Solar Power Plants | % of circular inputs for solar power plants Process: Number of solar panel components reviewed Process: Number of components reviewed for technical requirements | % of solar panels designed in accordance with circular design principles Process: Number of supplier consultations held regarding circular design for solar assets | % of solar panels recovered % of solar panels included in the circular decommissioning plan |
| Thermal Power Plants | % of circular inputs in components sourced for maintenance and repair of thermal power plants Process: Technical review of materials purchased for maintenance and repair | % of components used in repairs aligned with circular design principles Process: Number of supplier consultations held regarding circular design for components | % and weight of waste generated by hydroelectric plants (from landfill and incineration facilities 19) |
| Hydroelectric Power Plants | % of circular inputs in components sourced for maintenance and repair of hydroelectric power plants Process: Technical review of materials purchased for maintenance and repair | % of components used in hydroelectric maintenance aligned with circular design principles Process: Number of supplier consultations held regarding circular design for components | % and weight of waste generated by hydroelectric plants (from landfill and incineration facilities 19) |
| Construction Sites | % of circular inputs sourced for construction sites Process: Number of components reviewed for technical requirements Process: Number of materials reviewed for substitution | % of construction sites designed in line with circular design principle | s% and weight of waste directed from construction sites to landfill and incineration facilities 19 |
| Headquarters and Offices | % of circular inputs for headquarters and offices | N/A | % and weight of waste directed from headquarters and offices to landfill and incineration facilities 19 |
Low Applicability: Situations where Enerjisa Üretim has limited influence.
Moderate Applicability: Situations where Enerjisa Üretim’s influence is limited, but certain opportunities still exist.
High Applicability: Situations with clear opportunities and no significant constraints.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of our sustainable generation strategy. We aim to maximize resource utilization while minimizing the environmental footprint of our operations. To this end, we prioritize energy- saving measures and carbon emission reductions across both our existing infrastructure and new investments. By combining our expertise in renewable energy generation with operational efficiency, we are implementing digitalization, electrification, and low- emission technologies in energy-intensive processes. Our pioneering projects, carried out at various scales and locations, not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also set industry benchmarks as innovative solutions. The key initiatives underway at our power plants are outlined below.
Integrated Flue Gas Treatment and Carbon Capture (CCUS) Project at Tufanbeyli Energy Hub
As part of our strategic transformation program aimed at increasing energy efficiency while lowering emissions, we are launching a leading project at the Tufanbeyli Energy Hub focused on integrated flue gas treatment and carbon capture technologies. This project targets reducing CO₂ emissions as well as other pollutants in flue gas, including sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ),through a multi-pollutant sensitive system approach.
The system, featuring innovative wet scrubbing technology, captures CO2 and NOₓ compounds simultaneously from flue gas and chemically converts them into organomineral liquid fertilizer. This process turns harmful emissions into a valuable input for agricultural production. This approach offers an innovative solution model fully aligned with the principles of the circular economy and decarbonization, integrating environmental responsibility with economic benefit.
Site preparations and the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process are complete, with pilot-scale implementation planned for 2026. During this phase, the system’s modularity, chemical conversion efficiency, energy input impact, and compliance with national regulations will be thoroughly evaluated. Lessons learned from the pilot will provide the foundation for replication strategies at other thermal power plants with similar flue gas compositions near agricultural areas.
This technology moves beyond traditional sulfur treatment systems, positioning the Tufanbeyli Energy Hub, a critical part of energy supply security, as a leading example of transformation aligned with Türkiye’s climate goals.

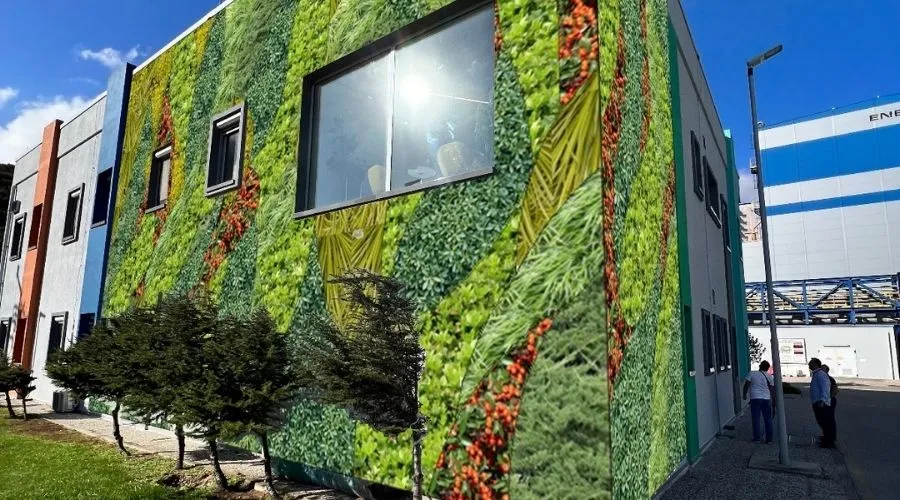
Bandırma-1 Administrative Building: Carbon Neutral and Green Building Transformation
As part of our efforts to support energy efficiency through structural transformation projects, an integrated energy management system based on carbon-neutral and green building principles has been implemented at the Bandırma-1 Administrative Building. The project targets powering all administrative building operations entirely with renewable energy sources and achieving net-zero emissions at the building level.
Solar panels and wind turbines have been installed on the building’s roof area, complemented by two Pomega hybrid containers deployed for energy storage. The system, with a total installed capacity of 90 kW, meets the building’s lighting, ventilation, and HVAC needs, ensuring energy demand is decoupled from fossil fuels.
A soilless vertical garden system on the building’s façades enhances natural insulation, while irrigation for the green façades is supplied with rainwater harvested from the roof.
All systems are centrally monitored through the Building Management System (BMS),with real-time tracking of energy generation, consumption, and water use via digital platforms. Launched in June 2024, this innovative application directly contributes to local carbon reduction and resource efficiency goals, serving as a benchmark for scaling sustainable building practices across the corporation.

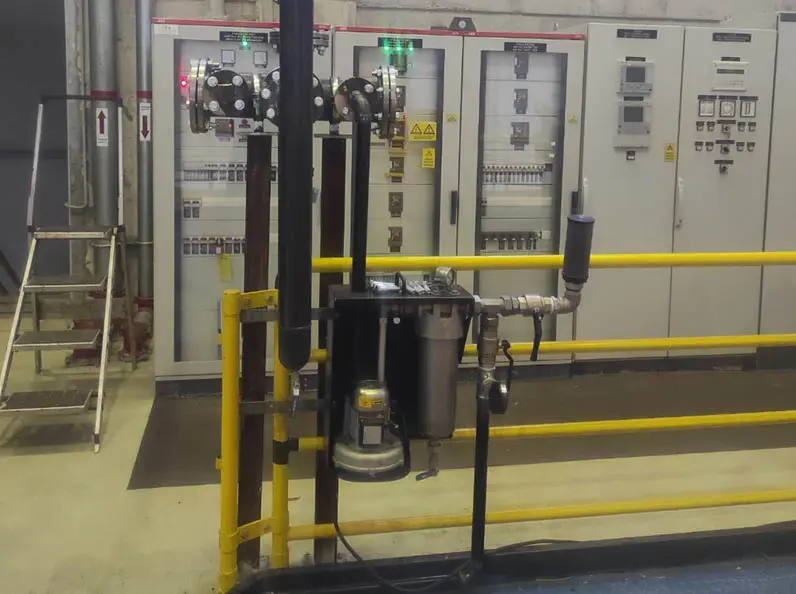
Yamanlı Hydroelectric Plant: Oil Mist Filtration System for Emission Reduction
As part of our preventive measures to reduce operational emission sources, an advanced Oil Mist Filter system has been implemented at the Yamanlı Hydroelectric Plant to control oil vapor released from machinery. This system plays a crucial role in preventing oil-based aerosols, especially those originating from rotating equipment, from dispersing into the air, thereby significantly improving both occupational health and environmental quality.
The filtration system effectively separates oil particles from the air, creating a clean and breathable environment within the work area. This application is strategically important not only for worker health but also for extending equipment lifespan and enhancing operational safety.
The collected oil is periodically drained and disposed of in compliance with hazardous waste management protocols.
The project offers a cost-effective yet highly efficient solution to minimize environmental emissions at hydroelectric production facilities. It is also considered part of a broader transformation vision aimed at integrating sustainable production standards across all our plants.

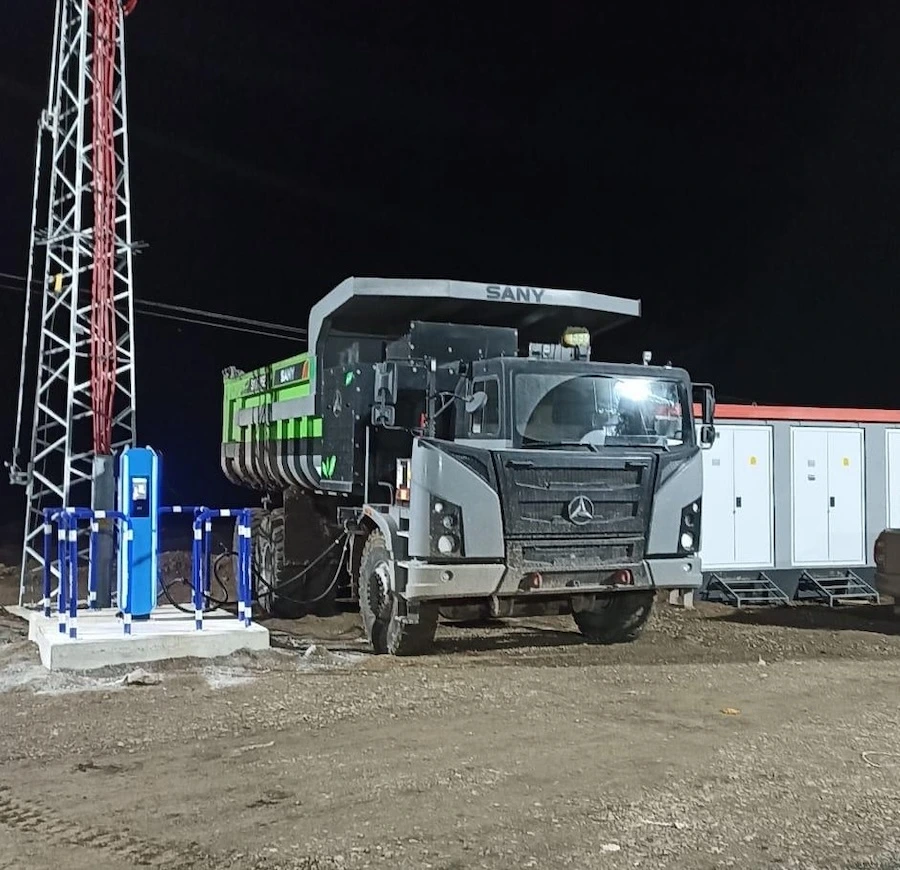
MadenNEXT: Transforming Mining through Electrification and Smart Operations
The MadenNEXT initiative at the Tufanbeyli Energy Hub was launched to reduce the carbon footprint and enhance operational efficiency by electrifying mining operations. The project aims to eliminate upstream Scope 3 emissions generated by diesel-powered vehicles, thereby restructuring carbon-intensive activities in line with the EU Taxonomy’s sustainable transition framework.
The first phase of this transformation was successfully completed with the deployment of five electric trucks, each equipped with a 564 kW battery capacity, and two electric excavators. These vehicles are actively operating on site, contributing not only to emission reductions but also to lower fuel consumption, decreased noise levels, and reduced risk of vibration-related workplace accidents.
The electrification effort extends beyond vehicles, with a
comprehensive redesign of the entire energy infrastructure to be supported by renewable and smart systems. The mine site will become an integrated, renewable-powered operation through the installation of a solar power plant, battery energy storage systems, and autonomous operation technologies. Notably, Türkiye’s first remotely controlled Stacker/Reclaimer equipment has been successfully commissioned, alongside the launch of digitization-driven automation processes.
Scheduled for completion by the end of 2025, the MadenNEXT project represents a transformative model that goes beyond cutting carbon emissions. It aims to deliver safer working conditions, lower maintenance costs, and long-term energy independence. Feasibility studies conducted within the project provide valuable insights into the efficiency and scalability of electric infrastructure, laying the groundwork for similar site transformations in the future.

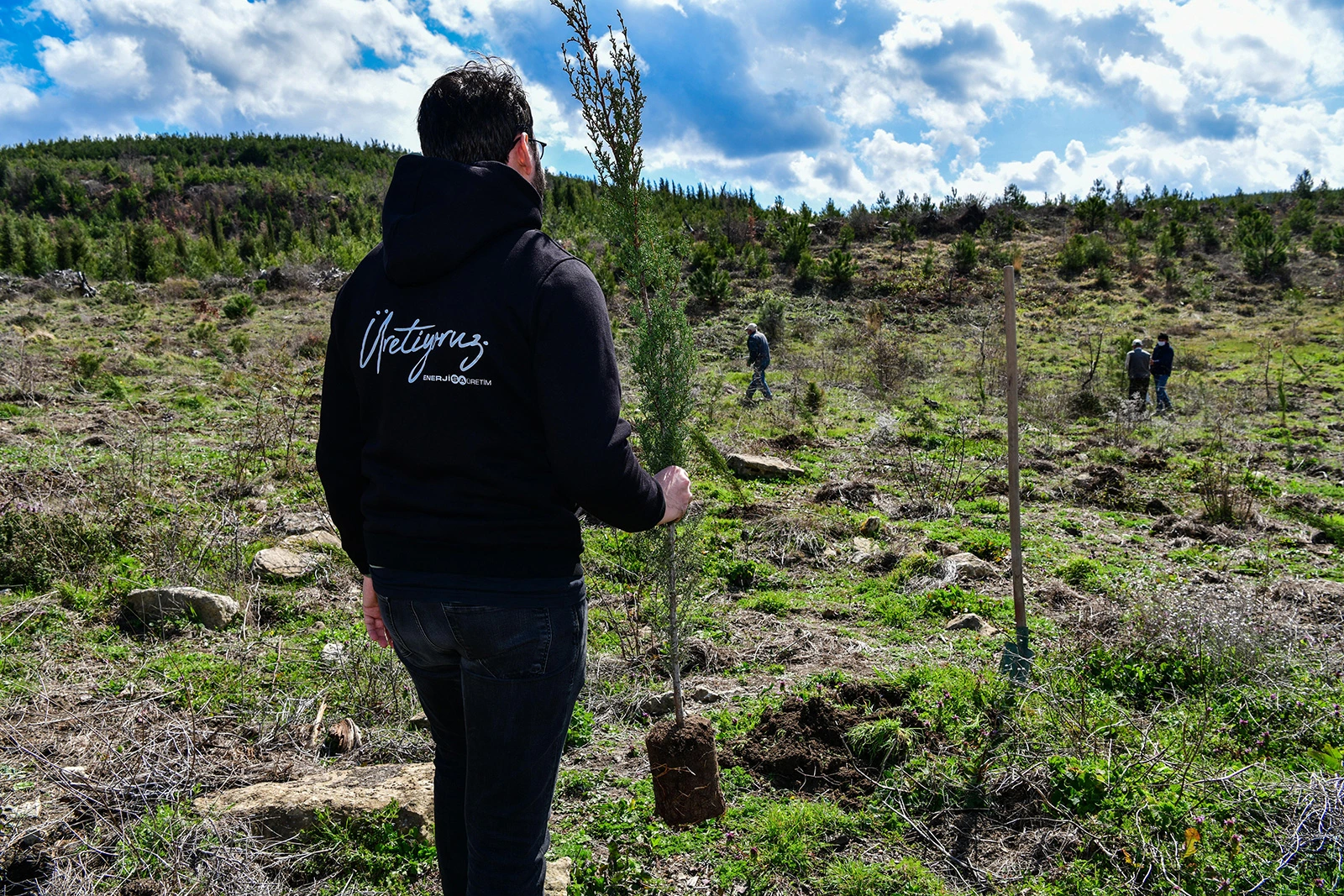
Afforestation Activities
Between 2019 and 2024, we planted a total of 1.3 million saplings across the impact zones of our Renewable Energy Resource Areas (YEKA) projects and operational sites. This effort transformed approximately 856 hectares, equivalent to 1,200 football fields, into forested land, making a significant contribution to the ecosystem.
To help preserve the natural ecosystem, we planted 280,000 saplings as a breath of fresh air for the future. Each year, we planted saplings equivalent to 10,000 times our age. Through our afforestation projects, we not only increase green spaces but also maintain ecological balance in the regions, creating long-term carbon sink areas.
Our sapling planting initiatives extend beyond just physically increasing forested areas; they also focus on spreading environmental awareness. Through training and awareness campaigns, we aim to raise local community consciousness—especially among young generations—to adopt sustainable lifestyles. These educational programs cover topics such as nature conservation, biodiversity support, and the importance of combating climate change, reinforcing a sense of environmental responsibility.
When selecting saplings, we prioritized species compatible with the local natural ecosystem that can contribute positively in the long term. The chosen saplings are resistant to frost and minimally affected by potential wildfire due to their thick bark. Additionally, species with economic value and industrial use were selected to support the local economy. This approach ensures a sustainable balance between regional development and ecological preservation.
The growth of the saplings is carefully monitored. Once mature, these trees will create new carbon sink areas, helping reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. Enerjisa Üretim aims to increase its sapling planting target to 2 million by the end of 2026, advancing our goals for ecological restoration and carbon reduction. We remain steadfast in our commitment to nature-aligned sustainable growth.
Within the scope of Sabancı Holding’s Youth Mobilization initiative, we organized, 1,3 a large-scale tree planting event at İzmir Institute of Technology with participation from our employees, university students, and academic staff.
This event was designed to raise environmental awareness among youth and employees while contributing positively to nature. Participants gathered on the university campus to reinforce the importance of contributing to a sustainable future.
The saplings planted during the event were selected from species suited to the region’s climate and soil conditions and aimed to support ecosystem balance. These species were chosen to integrate with the local flora and create carbon sink areas over time, reducing carbon emissions. As the saplings mature, they will also support local biodiversity and establish a natural habitat within the campus grounds. Enerjisa Üretim will continue to support projects that enhance environmental awareness among younger generations and uphold our responsibility to nature through events like this. Moving forward, we plan to expand similar initiatives, further strengthening our positive impact on both nature and society.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Management
We address the environmental impacts of our energy generation activities not only in terms of legal compliance but as a core element of our corporate strategy. Biyoçeşitlilik yönetimini; IFC Performans Standardı 6 (PS6),Avrupa İmar ve Kalkınma Bankası (EBRD) Performans Gerekliliği 6 (PR6),GRI 304 göstergeleri, Avrupa Yeşil Mutabakatı ve AB Habitat/Kuş Direktifleri gibi uluslararası standartlarla uyumlu şekilde yürütüyoruz.
The year 2024 marked a pivotal milestone for integrating biodiversity management into our corporate framework. As part of this, we appointed a dedicated corporate biodiversity specialist reporting directly to leadership team within our ESG structure. This step both strengthens our institutional capacity and establishes a solid foundation for embedding biodiversity management throughout our operations and investments. We completed the “Biodiversity Governance Document” in 2024 and plan to implement it company-wide starting in 2025. This document clearly defines our biodiversity management responsibilities, from investment decisions and site planning to construction activities and post-operation monitoring.
Enerjisa Üretim’s operational model for biodiversity management is based on the mitigation hierarchy approach promoted by financiers such as IFC and EBRD: avoid, reduce, restore, and offset/compensate. We integrate site-specific, ecosystem-based, and impact-assessment-driven biodiversity management into our decision-making processes through data- driven governance. At all operational sites, we conduct comprehensive monitoring and measurement activities to protect wildlife and maintain ecosystem balance. These efforts allow us to continuously track environmental impacts, identify potential risks early, and implement preventive actions. Monitoring and conservation activities include habitat use, population status, and threat analyses, which form the basis for Biodiversity Management Plans (BMP) for 2025.
Enerjisa Üretim continues its comprehensive monitoring, protection, and rehabilitation work to preserve biological diversity and sustain ecosystem balance.
Site-Based Monitoring Activities
- Our Wind Power Plants (WPP): Fixed-point bird observations and transect counts are conducted, while bat activity is recorded over extended periods using passive acoustic detectors. Data are analyzed with collision modelling, applying shutdown on demand and curtailment strategies when necessary.
- Our Hydroelectric Power Plants (HEPP): Monitoring of phytoplankton, benthic invertebrates, water quality, and other biological parameters is conducted, integrated with conservation strategies aligned with the EU Birds and Habitat Directives.
- Our Solar Power Plants (SPP): Flora and terrestrial fauna, especially site-specific species compositions and habitat preferences, are monitored. Data on endemic and sensitive species guide habitat restoration and nature-based solutions.
- Post-Construction Fatality Monitoring (PCFM): Beyond turbine areas, transmission lines and support.
Through these efforts, we have become one of Türkiye’s pioneering energy companies to embed the concept of nature-positive transformation into business models. Maintaining continuous alignment with international financial institutions and sustainability standards remains a fundamental principle of our company.
Biodiversity and TNFD-Aligned Management Strategy
Biodiversity loss is emerging as one of the most critical sustainability risks for companies and societies alike. As highlighted in the World Economic Forum’s 2024 Global Risks Report, this risk ranks among the top three threats facing our planet over the next decade.
We address the environmental impacts of our energy generation not just through regulatory compliancebut as a core component of our corporate strategy, financial planning, and sustainability performance. We proactively integrate biodiversity management across all operations, rigorously analyzing dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities related to nature.
Analysis of Nature-Related Impacts under TNFD and LEAP FrameworkTNFD ve LEAP Çerçevesi ile Doğa
Our biodiversity management approach is aligned with the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) framework, which advocates a nature-based risk and opportunity disclosure system. The TNFD’s four-step LEAP framework (Locate – Evaluate – Assess – Prepare) enables us to systematically assess our dependencies on nature and environmental impacts.
Accordingly, we follow these steps:
- BLocate: We identify the areas where our operations interact with natural assets.
- Evaluate: We examine the dependencies and impacts in these areas through both quantitative and qualitative analyses.
- Assess: We prioritize the risks and opportunities arising from the identified dependencies and impacts.
- Prepare: Based on these assessments, we develop action plans and make strategic decisions.
By integrating this framework into our corporate processes, we comprehensively map, measure, and manage our dependencies on ecosystem services and the impacts of our operations on natural capital across all our plants.
Identification of Priority Areas and Sensitivity Analysis
To better understand our plants’ interactions with nature, we employ a variety of scientific and geo- analytical tools aligned with TNFD’s definition of “priority areas.” The primary tools used include:
- EENCORE: Nature-based impact and dependency assessment
- WRI Aqueduct: Measurement of water risk and stress levels
- IBAT:Data on protected areas and threatened species
- Corine Land Cover:Land use, habitat fragmentation, and vegetation analysis
- FEOW: Freshwater ecosystems and distribution of migratory species
Sector prioritization is determined based on an analysis of Enerjisa Üretim’s process impact factors and dependencies. This prioritization relies on evaluating Enerjisa Üretim’s operations through ENCORE’s process categories, impact drivers, and dependencies on biodiversity and nature.
Identifying potential impact drivers on natural capital and biodiversity is crucial in Enerjisa Üretim’s process of selecting the most effective strategies to prevent, minimize, remediate, or offset its impacts on biodiversity. Similarly, recognizing dependencies on natural capital and biodiversity enhances Enerjisa Üretim’s ability to determine the most appropriate strategies to mitigate risks arising from these dependencies.
Management of Dependencies on Nature and Our Environmental Impacts
Our energy generation activities depend on ecosystem services at varying levels. In particular, our hydroelectric plants are directly reliant on the continuity of the water cycle and the healthy functioning of river ecosystems. The efficiency and operational safety of our thermal power plants are sensitive to environmental factors such as climate conditions, air quality, and water resources.
For all our plants, we analyze essential ecosystem services, including water supply, regulation of air and water quality, and soil erosion prevention.By assessing how changes in these services affect our operations, we develop business continuity plans that take these dependencies into account. The key dependencies we identify, in accordance with Science Based Targets Network (SBTN) criteria, comprise the environmental assets and services necessary for the safe and sustainable operation of our plants.
We also monitor and manage our impacts on nature based on the specific ecosystem conditions of the regions where we operate. Especially for large-scale renewable energy projects, we carefully manage site selection processes to reduce habitat loss and fragmentation risks, supported by environmental and social impact assessments.
Direct impacts such as the effects of wind turbines on birds and bats, alterations caused by hydroelectric plants to river ecosystems, and land use pressures from solar plants are evaluated through on-site biological monitoring. For example, migratory bird routes and bat activity are regularly tracked, with turbine-related risks analysed based on collected data. Additionally, we conduct field inspections to manage the risk of invasive species spread and raise awareness among our employees on this issue.
We also consider the indirect effects of climate change on ecosystems. Anticipating that changing climate conditions may alter migration and breeding cycles for certain species, we develop adaptation and mitigation strategies accordingly.
All these efforts are supported by analyses conducted with the ENCORE tool, aligned with TNFD and SBTN frameworks. The table below summarizes the priority impact and dependency areas according to the energy generation technologies we employ.
Ecological Sensitivity studies have been conducted under three main categories, yielding the following results across all Enerjisa Üretim power plants:
Based on the analysis results, a significant portion of Enerjisa Üretim’s sites, 38%, are located in areas facing very high water-related threats, while 57% are situated in regions with high water risk. The water risk indicator used in the analysis was calculated using the World Resource Institute (WRI) Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas Tool, which integrates selected indicators from categories such as physical quantity, quality, regulatory, and reputational risks to measure all water-related risks comprehensively.
WRI Map
Taking into account international biodiversity and natural capital frameworks such as the SBTN and TNFD recommendations, Enerjisa Üretim has identified the biodiversity impact zones and risks of its power plants by utilizing tools and databases like ENCORE, IUCN, and WRI. In light of these detailed analyses, Enerjisa Üretim is working on a roadmap to neutralize biodiversity risks in its operational areas with a responsibility toward tomorrow. As a result of these analyses, nine priority sites4 have been identified where particular sensitivity exists regarding biodiversity and water usage. These sites have undergone detailed assessments to further examine related biodiversity risks and opportunities.
Assessment of Nature-Related Risks
Our impact areas point to various nature-related risks for Enerjisa Üretim. In alignment with the TNFD approach, our company conducts risk assessments based on scientific methods and data. The main nature-related risks are as follows:
- Risk of Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Especially for renewable energy projects like wind and solar, inappropriate site selection may cause habitat fragmentation or damage to critical habitats. This risk is minimized through comprehensive ecological assessments conducted prior to investment.
- Species-Related Risks: Our operations may negatively affect living things such as birds, bats, and fish. For example, risks of population decline due to turbine collisions or changes in water regimes are managed through continuous monitoring and conservation measures.
- Invasive Species Risk: Unintentional spread of non- native or invasive species through site activities could threaten local species. This risk is mitigated via site control programs and biosecurity protocols.
- Climate Change and Secondary Impacts: Extreme weather events, droughts, or ecosystem degradation caused by climate change may increase operational risks. Consequently, climate-related risks (e.g., changes in hydrological cycles) are included in our nature risk inventory and addressed integrally through adaptation policies.
By the end of 2024, with expert consultancy support, we completed a Nature Risk and Opportunity Inventory study for key investment sites. This study involved detailed ecosystem and biological component analyses, prioritizing ecosystem services, habitat integrity, and species-based risks. The analysis follows TNFD recommended criteria and provides a solid foundation for more systematic corporate-level risk management. From 2025 onwards, we aim to deepen these inventory results and develop risk reduction action plans for each high-priority site. This will ensure consistent identification, monitoring, and management of nature-related risks throughout the company.
Assessment of Nature-Related Opportunities
Enerjisa Üretim approaches biodiversity conservation not only from a risk management perspective but also as a source of potential new opportunities. Protecting and enhancing natural capital presents long-term value- creating prospects for our company and stakeholders. Within this framework, our key opportunity areas are as follows:
- Ecological Restoration and Habitat Improvement: To minimize the environmental impact of infrastructure projects, we integrate ecological restoration activities. At all investment sites, seeds of local flora species are collected and delivered to the Turkish Seed Gene Bank under the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry. Through these efforts, our projects contribute to preserving and passing on the biological richness of affected ecosystems, not only compensating for negative impacts but also aiming for a net positive contribution to ecosystems.
- Reputation, Stakeholder Trust, and Financing Access: Strong biodiversity performance is a critical factor that enhances our corporate reputation and strengthens stakeholder trust. Our achievements in nature conservation increase confidence among investors and lenders, facilitating access to sustainable financing instruments.
The Mitigation Hierarchy serves as our primary guide for implementing corporate strategy in the field. This approach, mandated by institutions such as IFC and EBRD, offers a four-tiered priority framework for managing negative impacts from operations: avoidance, reduction, rehabilitation/restoration, and offset/compensation. Enerjisa Üretim prioritizes the principle of “avoidance” when launching new projects or investments by aiming to steer clear of sensitive areas with high biological value. For example, during planning of wind farms, locations presenting overlap risks with Key Biodiversity Areas, critical habitats, or protected areas are reassessed to eliminate such risks. In 2024, detailed habitat mapping and critical species distribution analyses conducted for some wind projects preparing for construction led to relocation decisions for several turbines, thereby protecting endemic plant communities and wildlife within the project sites.
During the reduction phase, proactive measures are taken during construction and operation to minimise unavoidable impacts. For instance, a bird collision risk analysis conducted in 2024 at the Ihlamur Wind Energy Plant indicated that nearby high-voltage transmission lines may pose threat to large bird species such as the white- tailed eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla),Dalmatian pelican (Pelecanus crispus),and great white pelican (Pelecanus onocrotalus). Following this finding, coordination with the grid operator TEİAŞ initiated the installation of “flight diverters” on the transmission lines to alter birds’ flight paths and reduce collision risks. This action represents a concrete step to lessen bird mortality related to energy transmission infrastructure.
In the rehabilitation/restoration phase, we focus on restoring habitats that have been inevitably disturbed or damaged by our activities. For example, pre- construction flora studies at our Harmancık Wind Energy Site identified an endemic plant species, Verbascum hasbenlii, which inhabits rocky habitats unique to Türkiye. To protect this species, microhabitats it occupies were excluded from the work area to prevent direct habitat loss. Additionally, seeds of this species were collected and sent to the Turkish Seed Gene Bank for ex-situ conservation.
Regarding the fourth and final phase, offset/ compensation, although applicable standards in Türkiye still vary by species and are not yet fully established, Enerjisa Üretim aims to initiate feasibility and planning studies for potential offset projects that may be required in the future. In this context, we plan to carry out technical analyses and policy development activities in 2025 and beyond at selected pilot sites to test potential “No Net Loss” (NNL) approaches. Our current practices under IFC Performance Standard 6 (PS6) and EBRD Performance Requirement 6 (PR6) lay the groundwork for implementing the NNL principle. In the upcoming period, we will assess net impact-offset scenarios, particularly at specific wind power plants. Through these efforts, we aim to establish the corporate infrastructure required for a mid-term transition to nature-positive business models and to position ourselves as a pioneer in the sector.
Stakeholder Engagement Approach
Enerjisa Üretim believes sustainable biodiversity management is achievable only through active involvement and collaboration of all stakeholders. Accordingly, stakeholder engagement is managed transparently, inclusively, and effectively.
Our biodiversity management processes are open to active participation from stakeholder groups based on transparency and shared decision- making principles.
We collaborate closely with public institutions, particularly the Ministry of Environment, Urbanization and Climate Change and the Directorate General of Nature Conservation and National Parks (DKMP). Ecological risk assessments, habitat analyses, and conservation activities are conducted jointly with these institutions. For example, during our nest identification efforts at the Aydos Wind Energy Plant, a white-tailed eagle nest was discovered outside the project’s impact zone but within the surrounding area. The location was shared with DKMP, and relevant information was provided to initiate necessary conservation measures.
Our biodiversity impact assessment studies are publicly available on our corporate website. Additionally, we maintain regular communication with various NGOs for consultation. For instance, under our Harmancık Wind Project, we have taken significant steps to conserve Verbascum hasbenlii, a region-specific endemic species, collaborating with the relevant Ministry and universities to support sustainable protection of its natural habitat.
Project ecosystem impacts are regularly evaluated according to IFC and EBRD standards, with results shared transparently with financial institutions. Monitoring data and biodiversity performance are reported regularly, and feedback from financial stakeholders is used for continuous improvement.
For all projects subject to financing, we conduct comprehensive biodiversity screening studies. These include detailed investigations focused on minimizing our projects’ effects on natural ecosystems, covering four key areas: ornithology (bird monitoring),bat monitoring, Biodiversity Action Plans (BAP),and collision risk modelling.
Enerjisa Üretim continues to advance its efforts to protect biodiversity and natural environments without pause.

Site-Based Practices and Biodiversity Programs
Enerjisa Üretim’s biodiversity strategy is reinforced through concrete, site-based practices, with tailored approaches developed for each type of project. For our hydroelectric, wind, solar, and thermal power plants, located across diverse geographical regions, specific ecological risks and opportunities have been identified, and comprehensive programs have been implemented accordingly. Below is a summary of the key site-based biodiversity management programs applied across our entire portfolio:
Biodiversity in Our Wind Power Plants
Our wind power plants inherently pose potential interaction risks with flying wildlife, particularly birds and bats, which is why ornithological and bat monitoring programs are standard practice at these facilities. Expert biologists conduct bird observations during breeding and migration seasons using fixed- point and transect count methods, while passive ultrasonic detectors record bat activity within the same areas. Utilizing this data, collision risk models for bird and bat species are developed for each site. If elevated risks are identified for specific species, mitigation measures such as Shutdown on Demand or operational curtailment during critical periods are implemented. These proactive steps aim to minimize collision risk by halting or reducing turbine speeds during peak wildlife activity. Additionally, in 2024 we expanded our Post-Construction Fatality Monitoring (PCFM) programs to cover not only turbine areas but also the energy transmission lines and other supporting infrastructure. During the planning phase of our wind projects, critical habitat surveys are conducted, and when endemic or endangered species are detected, project designs are adjusted accordingly. For instance, biodiversity studies at the Kestanederesi Wind Power Plant identified rare invertebrates such as Chorthippus bozdaghensis, a grasshopper unique to the region, and the Apollo butterfly (Parnassius apollo). Tailored monitoring programs have been developed for these species. This approach helps ensure our wind investments provide relatively safe habitats nationwide, striving to harmonize energy generation with wildlife conservation.
Biodiversity in Our Solar Power Plants
Given the extensive surface areas covered by our solar power plants, we place special emphasis on assessing their impact on local habitats. Flora and terrestrial fauna studies are prioritized both before and after installation at our solar sites. Each solar plant’s regional species composition, presence of endemic and sensitive species, and the effects of land-use changes on ecosystems are carefully analyzed. To prevent complete removal of vegetation and enhance existing habitats, we design panel layouts that allow native plants to grow in the spaces between arrays.
Protection of Aquatic Ecosystems in Our Hydroelectric Plants
Dedicated monitoring programs are in place to safeguard freshwater ecosystems impacted by our hydroelectric plants. Environmental flow regimes have been established at dammed hydroelectric projects to preserve aquatic life cycles. For plants without fish passages, fish ladders have been constructed, and a ‘Fish Capture and Transport System’ is utilized to facilitate migration. Other facilities with existing fish passages undergo continuous functionality monitoring. Water quality and sediment accumulation are regularly assessed, alongside seasonal fish monitoring studies. In 2024, our protocols were updated to align aquatic ecosystem monitoring with the EU Taxonomy Regulation, and biological indicators have been introduced, ranging from phytoplankton to macroinvertebrates. At Kandil, Yamanlı, and Arkun hydroelectric plants, collaborations have been established with universities and research institutions to study the long-term effects of hydrological changes and sedimentation. Our objective is to maintain ecological integrity while ensuring sustained energy generation, with the ability to implement protective measures swiftly when necessary.
Biodiversity in Our Thermal Power Plants
Within the scope of the extensive environmental modeling work initiated in 2024 for the Tufanbeyli Power Plant, air emissions, ash management, and waste impacts have been analyzed to identify potential risks to ecosystem health and air quality. Based on these analyses, additional filtration systems, improvements to ash storage areas, and environmental afforestation projects have been planned. Moreover, we aim to support species diversity through site-specific habitat restoration and micro-ecosystem enhancement efforts.
For the Bandırma Energy Base, a comprehensive marine ecology monitoring program has been conducted to assess the impacts of our deep-sea discharge activities on the Marmara Sea. As part of the extensive marine ecology study carried out in 2024, physical, chemical, and biological parameters were thoroughly analyzed in the water intake and discharge zones. The findings revealed that the artificial reef structures in these areas have supported the establishment of stable populations of species such as seabass, sand steenbras, and white grouper. Turbidity observed at the discharge points diminishes between 250 and 500 meters, indicating that ecosystem health is being maintained.
Thanks to our continuous monitoring systems, water temperature and quality are kept within habitable limits for marine life, with operational adjustments made as necessary.
Habitat Restoration and Ex-situ Conservation Projects
Across all our power plants, efforts to repair habitat damage caused during construction and operation are of critical importance. Enerjisa Üretim invests in projects focused on improving local ecosystems and protecting species in every region where it operates. At all sites where we conduct flora studies, seeds from significant and rare plant species are collected and delivered to the national gene bank in Ankara. Starting in 2025, we aim to implement on-site species conservation practices and, where necessary, species translocation (relocation to suitable habitats) in all new projects currently in the construction phase.

Arkun Wildlife Project
In collaboration with the General Directorate of Nature Conservation and National Parks, we are implementing technical measures in the Arkun Dam area to monitor biodiversity and advance wildlife conservation efforts. This ecologically important region is closely monitored for its ecosystems, plant and animal species, and biodiversity—including flora and fauna listed under national and international agreements. We continuously gather new, real-time data to build a comprehensive information database, which is analyzed and reported.
Among the key mammals in the area, we track the chamois population using satellite collars, recording their activity patterns. In 2024, we fitted female chamois, Yıldız and Sıla, with satellite transmitters and released them back into the wild. Regular signals from Yıldız and Sıla provide invaluable insights into their biological and physiological changes, habitat use, and movement routes. This information helps fill knowledge gaps and supports the development of effective biodiversity conservation policies. As the first in Türkiye to monitor chamois with satellite collars, Enerjisa Üretim proudly demonstrates its commitment to respecting wildlife and continues to pioneer innovative conservation initiatives.
To raise awareness about biodiversity and foster a wildlife culture, Enerjisa Üretim annually organizes an award- winning wildlife photography contest within the company through the Enerjisa Üretim Arts Club. In addition, we publish an online magazine titled “Yaban Hayatından İnciler”(Pearls from the Wild),which focuses on wildlife, flora, and fauna.
Nature-Based Risk and Opportunity Analysis in the Supply Chain
We do not limit our assessment of nature-related risks and opportunities to our operations alone; we evaluate them across our entire supply chain. As part of this approach, in 2024 we conducted a detailed analysis based on the TNFD’s LEAP methodology to examine our supply chain’s dependencies on nature and its impacts on the environment.
During the analysis, nine supplier companies were assessed, representing approximately 92% of our total procurement volume and carrying a high potential for nature-related risks. These suppliers were categorized by sectors with significant environmental impact, including construction, machinery and equipment manufacturing, mining, and energy equipment. Sector-specific evaluations identified key factors such as water usage, land conversion, reliance on biotic resources, and greenhouse gas emissions as critical drivers. Using the ENCORE tool, this dual analysis assessed both dependencies on nature and impacts on biodiversity.
Furthermore, by applying WWF’s Biodiversity and WRI’s Water Risk Filters, we developed risk profiles for the ecosystems, water stress, flood risk, and habitat integrity of the regions where these suppliers operate. The findings revealed that some supplier locations face moderate to high nature- related risks. This analysis served not only as an identification tool but also laid the groundwork for transparent and collaborative action planning. We shared the results with the relevant suppliers and have begun developing risk mitigation roadmaps together with each priority supplier. Through a process centered on mutual learning and continuous improvement, we strive to reduce nature-based risks and promote sustainable practices throughout our supply chain.
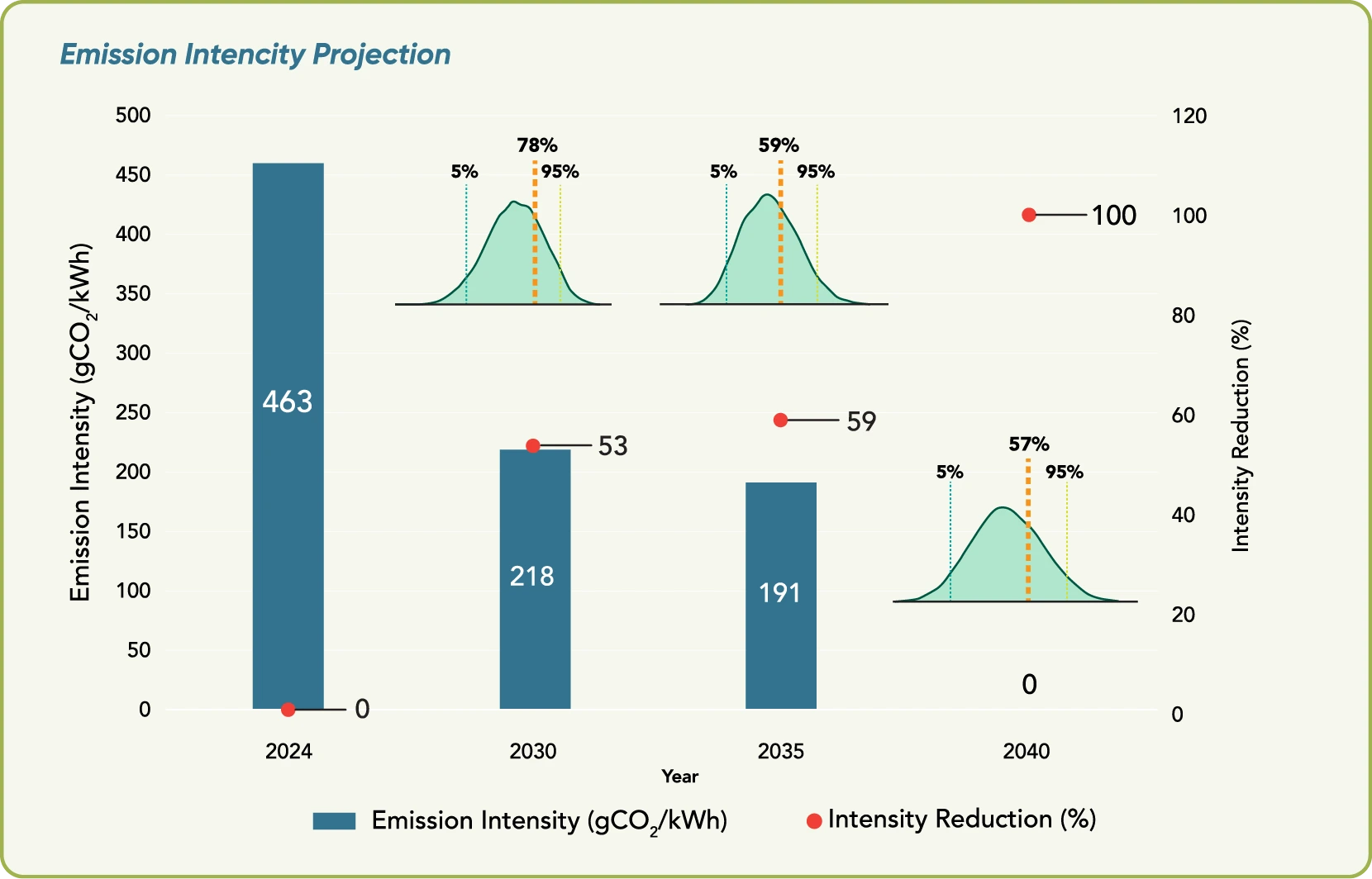
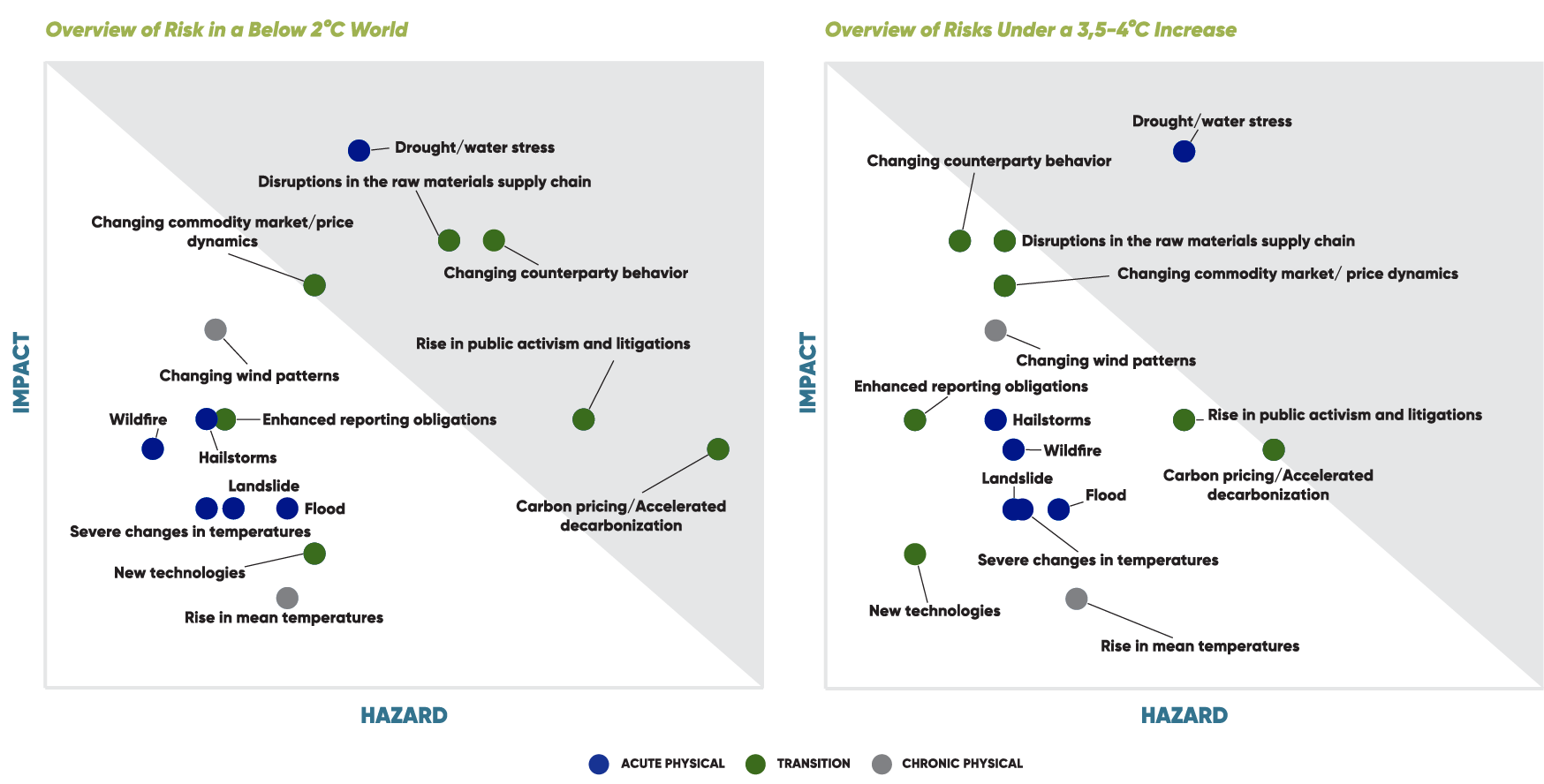
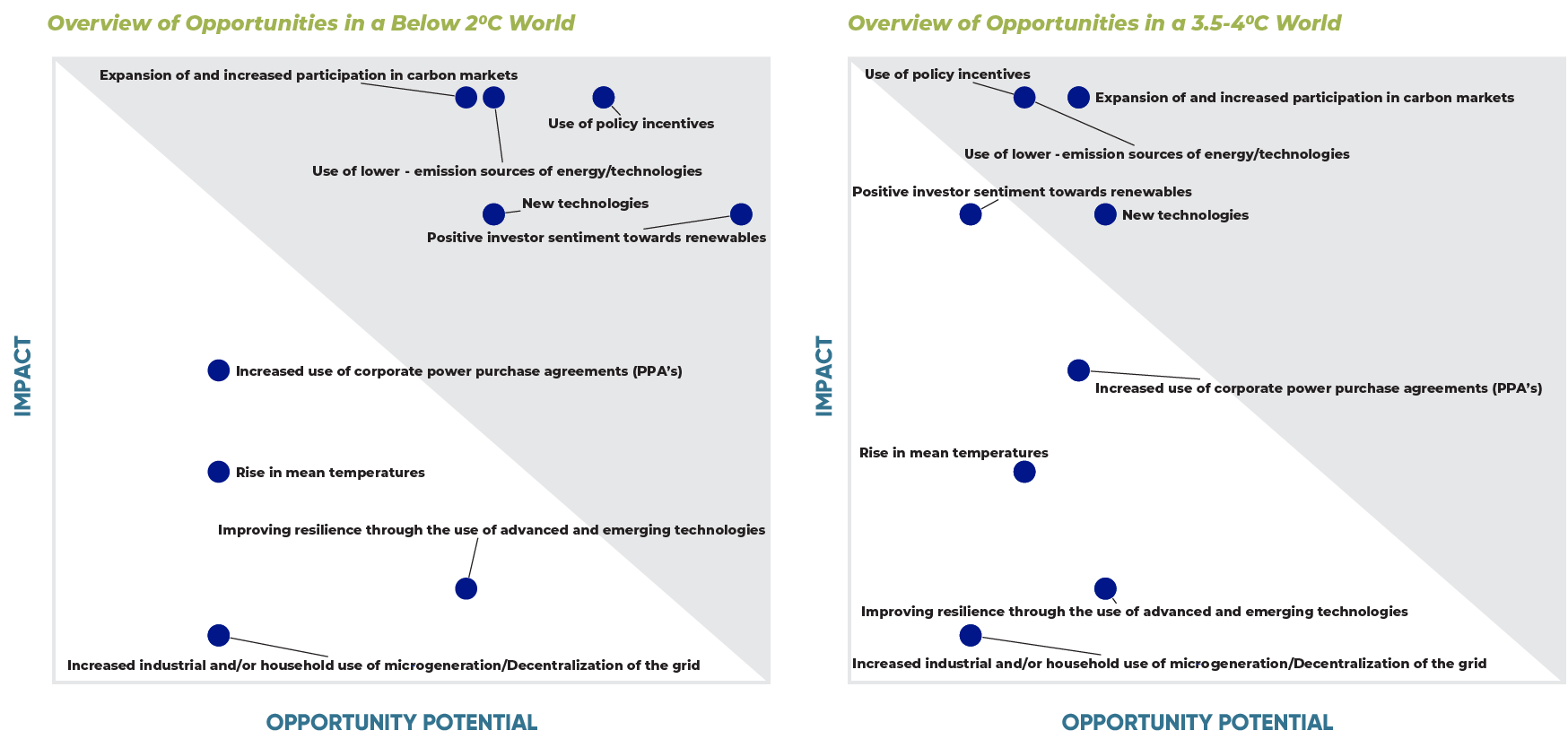
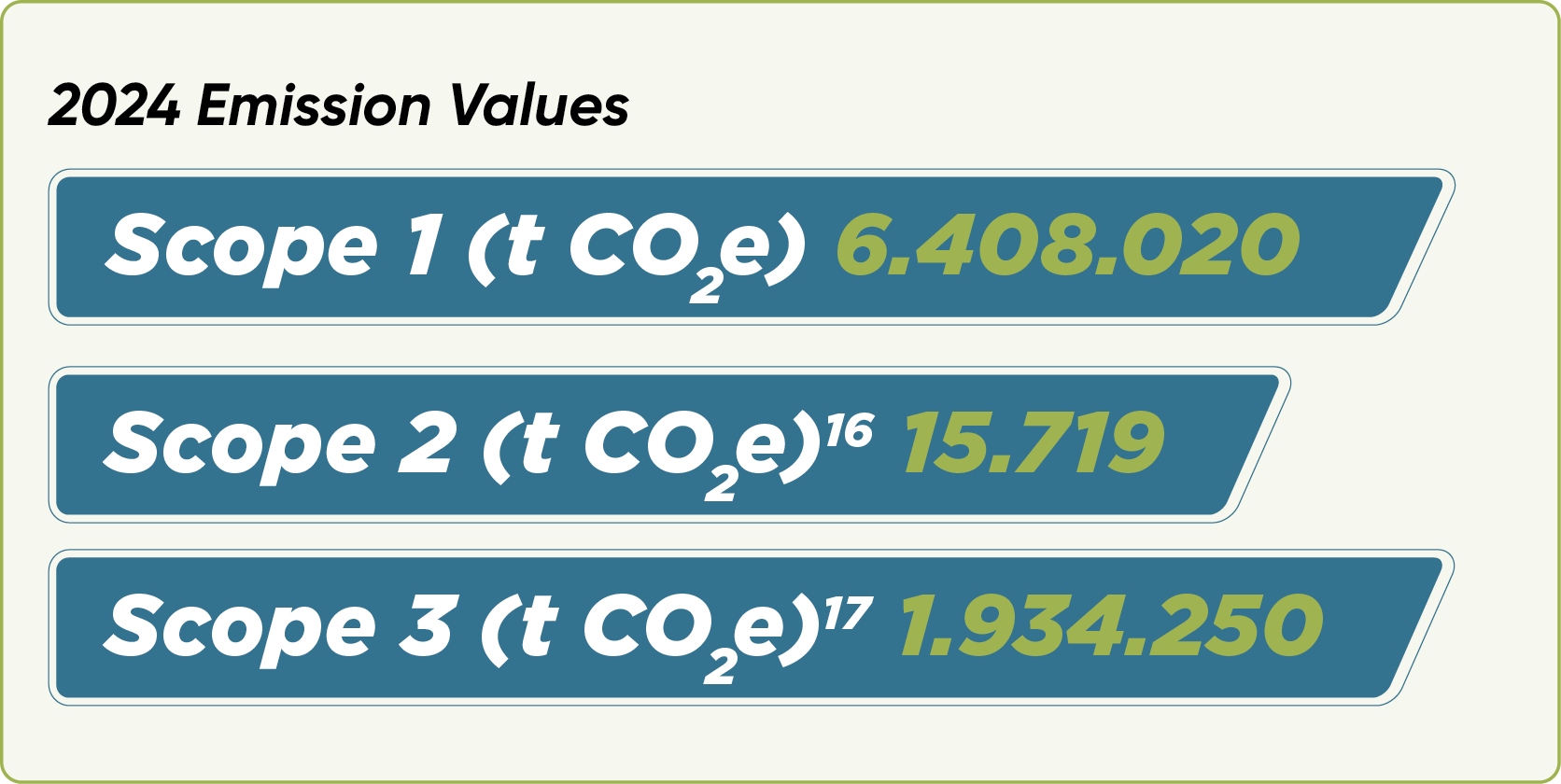
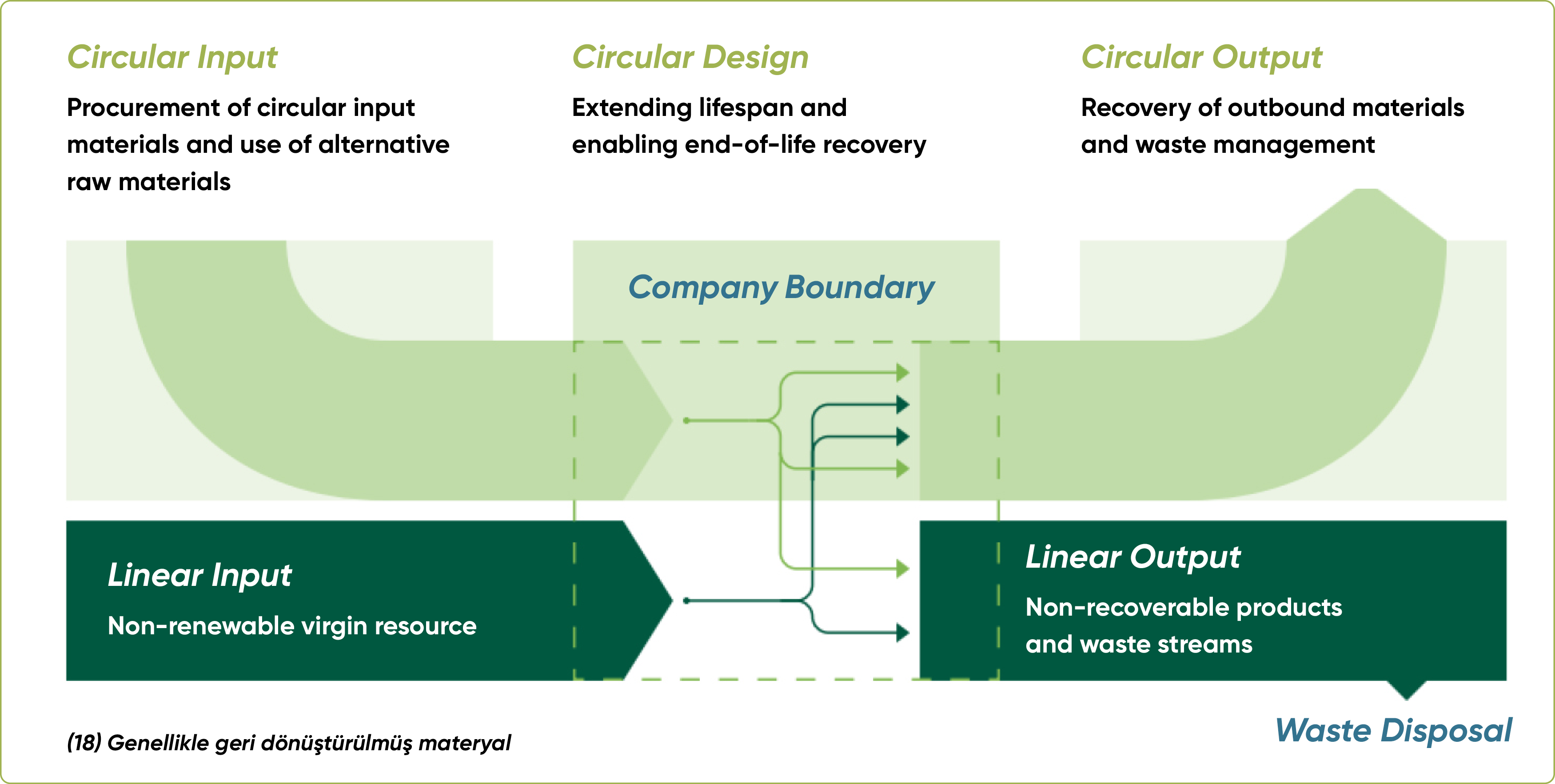

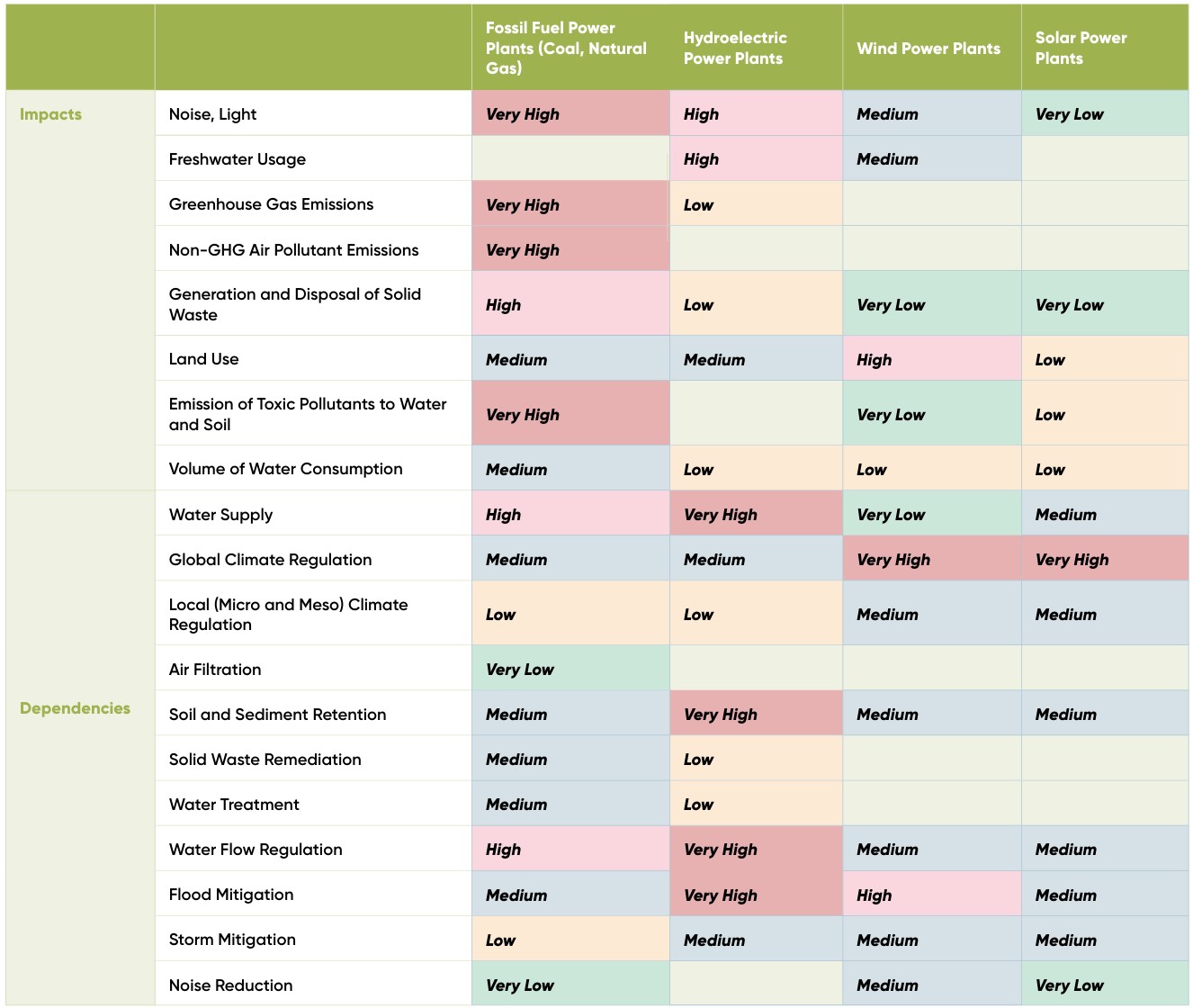
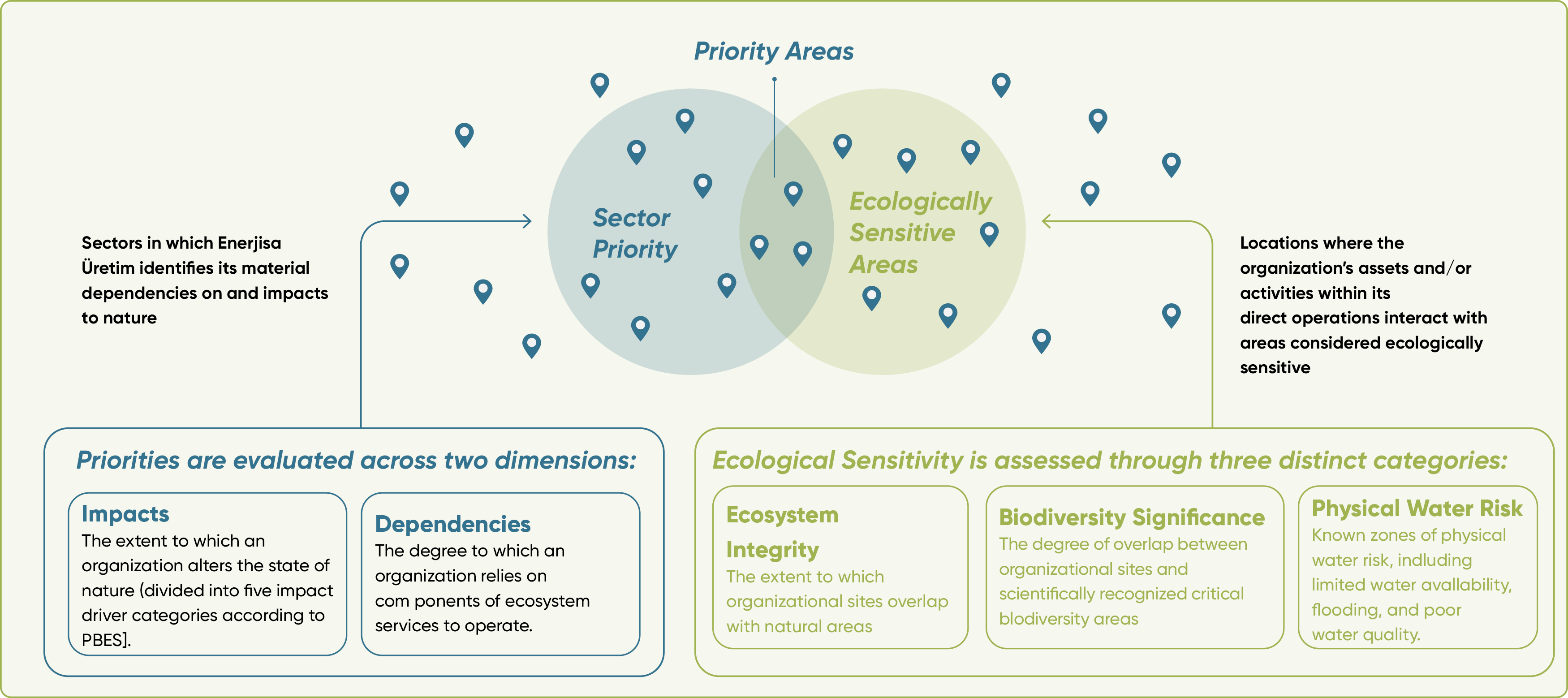
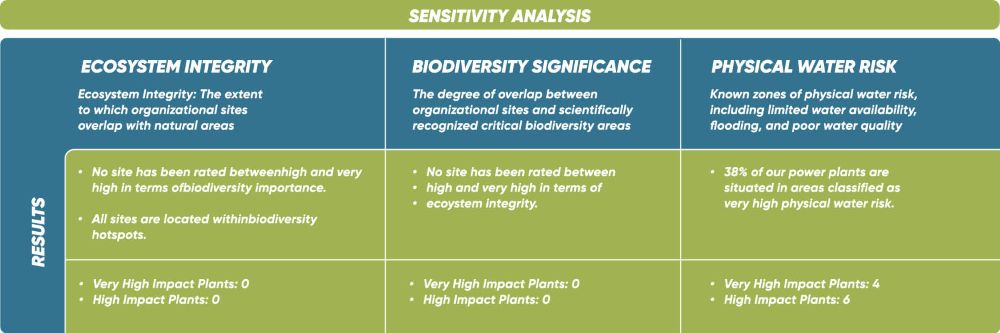
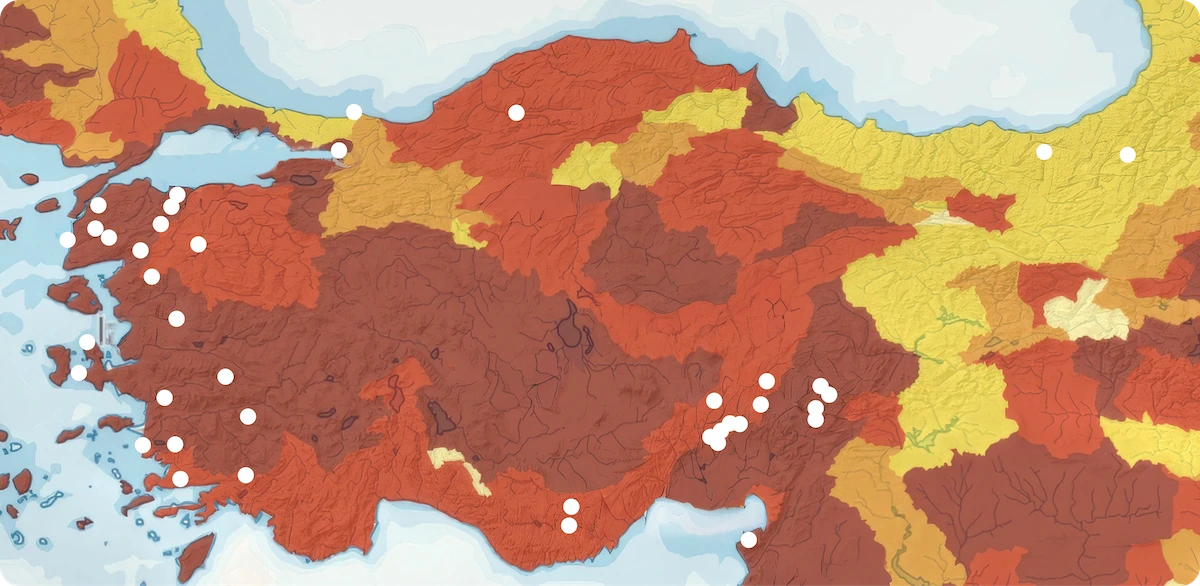
Social Responsibility and Community Contribution
As Enerjisa Üretim, we operate with a value creation mindset that goes beyond energy generation, placing social and environmental development at the heart of every region where we operate. Aware of our responsibility to society, we implement long-term social initiatives across numerous fields including equal access to education, local development, economic empowerment of women, access to healthcare, environmental protection, and biodiversity conservation. As of 2024, we have systematized our social contribution projects, particularly in the Tufanbeyli, Western Power Plants, and Erciyes regions, through a field-focused approach within our Corporate Social Affairs structure. These efforts, spanning from education and healthcare to regional agricultural development and sports activities, have directly benefited thousands of individuals. Designed in alignment with sustainable development principles, these projects prioritize enhancing social value and fostering growth alongside the communities where we live and operate.
Enerjisa Üretim’s social responsibility approach is fully aligned with the company’s sustainability vision, grounded in an impact-driven and holistic approach. This approach encompasses social support mechanisms that address local development, inclusive economic growth, environmental balance, and social equity together, aiming to achieve long-term transformative change. Our social support mechanisms are designed with sensitivity to local realities, focused on social impact, and developed through a stakeholder-inclusive planning approach, implemented in an integrated manner across defined thematic areas. Our activities not only respond to immediate needs but also seek to reduce risks, expand opportunities, and strengthen social resilience. Within this framework, we categorize our projects according to strategic priorities and manage them under a comprehensive impact management philosophy.
Shared Value Creation and Responsibility Projects
Our approach to social responsibility extends beyond simply meeting current needs; it is integrated into our corporate strategy as a structure that delivers long- term societal benefits. Accordingly, we manage our social investments through an integrated framework that includes impact management, grievance and demand handling, as well as project development and implementation, ensuring that these initiatives are planned and measurable. Our projects also serve as tangible and lasting tools on the ground, shaped by priority social themes.
In 2024, our budget allocated for community investment activities was planned and utilized in line with our thematic priorities. The annual distribution of resources based on these thematic areas is presented below.
In energy generation, managing the social impacts of transformation is just as much a priority as the transformation itself. In the regions where we invest in renewable energy, we diversify our social projects across themes such as climate-resilient livelihoods, water efficiency, biodiversity, and agricultural resilience. Accordingly, we approach social sustainability in conjunction with environmental sustainability and operational efficiency, aiming to align our energy generation processes with the local ecosystem. In doing so, we foster a model of local development that is not only economically sound but also climate-resilient and socially just.
With the establishment of the Corporate Social Relations Department as of 2024, we have shaped our social investments according to strategic priorities. By expanding our corporate capacity, we have systematized our processes. Within the new organizational structure we are developing and aligned with our social impact capacity, we have broadened the thematic areas that we previously focused on as social responsibility priorities, Women, Children, Trees, and Stray Animals, into Regional Development, Economic Empowerment and Employment, Gender Equality, Culture and Environment, Health and Social Welfare, and Education. Projects implemented under these themes are assessed both for the direct benefits they provide and for the systematic level of impact they achieve; these are reported in an integrated manner within the corporate performance indicators.
Based on our social responsibility and impact areas, we manage social impact through four core procedures: Social Impact and Relations Management, Social Investments, Demand and Complaint Management, and the Development and Implementation Procedure for Social Impact Projects. Within this framework, we have launched numerous community-focused projects across multiple locations through dedicated working groups within our sustainability structure.
Throughout 2024, the projects we implemented directly benefited more than 7,000 individuals. In our social investment planning, we actively use impact measurement tools such as SROI to highlight not only outputs but also outcomes and the broader social value created. This approach clearly demonstrates that our social strategy serves as a foundational pillar guiding decision-making across the organization and contributing to sustainable value creation.
Community Projects and Social Impact Analysis
In line with our understanding of social responsibility, we carry out various projects in education, healthcare, environment, and the sport. Through these projects, we develop programs that contribute to society. Additionally, by providing donations and infrastructure support, we aim to achieve sustainable development goals and support societal progress. In the regions where we operate, we implement impact assessments and development programs to support the social and economic development of local communities. We place importance on building strong relationships with local people and systematically manage these relationships in accordance with the following policies and procedures:
In line with the policies and procedures we implement, we regularly conduct social and environmental impact assessments in our power plant operations and project areas. By placing stakeholder engagement at the center of all these processes, we ensure ongoing communication with local communities through our Power Plant Administrative and Social Affairs Teams and Community Liaison Officers. Community Liaison Officers are employed in roles specifically structured for our YEKA wind power plant projects and operate in fields unique to these projects. We systematically record and evaluate requests, feedback, and complaints from our stakeholders, and develop sustainable solutions tailored to identified needs. We design our communication processes to cover our entire value chain and regularly review field-level practices to ensure continuous improvement.
We classify each social responsibility and community investment project based on clearly defined thematic priorities and implement them by prioritizing their potential for social contribution within these categories. For example, the Yahyalı Women’s Beekeeping Program, launched to support sustainable livelihoods, is categorized under the “Gender Equality” theme, while the Greenhouse Heating Project is directly linked to the goals of “Regional Development” and “Environmental Sustainability.” Our projects are designed not only to address current needs within the thematic framework, but also to deliver long-term value by mitigating risks, enhancing opportunities, and strengthening community resilience.
We structure our social responsibility approach to be responsive to regional needs, sustainability-focused, and impact-driven. Our aim is to make tangible and lasting contributions across key social sectors such as education, health, economic development, environment, cultural preservation, and sports.
We manage the projects we implement by mapping them to relevant SDG targets, ensuring our social impact is measurable, strategic, and oriented toward long-term outcomes. Below are the areas in which our projects operate, along with their corresponding SDG alignments:In the education sector, initiatives, focused on upgrading school facilities, supplying technical equipment, and enhancing student engagement. As part of these efforts, renovations and repairs at Soysallı Enerjisa Primary and Middle Schools have established healthier learning environments for students. The provision of camera traps to Bayramiç Vocational School has supported hands-on training opportunities. Furthermore, various equipment upgrades and event sponsorships at Enerjisa Science High School have contributed to the students’ academic success and social growth.
In the healthcare sector, efforts to improve access to medical services and strengthen infrastructure included donations of various medical devices, support for mobile health services, and volunteer- driven blood donation campaigns. Surgical equipment provided to Göksun State Hospital enhanced treatment capabilities, while technical equipment supplied to Tufanbeyli and Saimbeyli hospitals increased the efficiency of emergency healthcare services. Transportation support for home care and dialysis patients helped facilitate access to services in rural areas.
Under the themes of economic development and employment, agricultural infrastructure support has been provided to local producers, programs encouraging women’s entrepreneurship have been implemented, and initiatives aiding post-disaster recovery have been launched. The greenhouse heating project in Tufanbeyli promoted production through the use of renewable resources, while beekeeping support for women in Yahyalı contributed to rural development. Irrigation projects bolstered agricultural output, and infrastructure assistance was also extended to livestock farmers recovering from disasters.
Within the scope of environmental sustainability and cultural preservation, monitoring technologies have been employed to protect wildlife, and preventative infrastructure against forest fires has been established. Drone support was provided in Adana Yamanlı to aid efforts against illegal hunting, while a fire watchtower constructed at the Çanakkale Harmancık WPP site has enhanced early response capabilities.
In the field of sports, camps and club support programs have been implemented to promote the physical development of children and youth, while leveraging the unifying power of sports to encourage healthy lifestyle habits. Within this framework, a basketball camps organized in partnership with Enerjisa and its stakeholders, as well as cash grants to a sports club in Yahyalı, have been successfully carried out.
Since 2019, in collaboration with our stakeholders, we have reached more than 2,200 children under the motto “Our Energy is Basketball.” Through 14 different camps held across Türkiye, from Çanakkale to Kahramanmaraş, we provided children with basic basketball training, monitored their physical development, and organized activities that foster team spirit. While combining the unifying power of basketball with social responsibility at our camps, we also raised awareness on renewable energy and sustainability. To date, our camps have reached the cities of Çanakkale, Balıkesir, Aydın, Muğla, Adana, and Kahramanmaraş, providing thousands of children with basketballs, jerseys, and fundamental basketball training support. The key projects are highlighted above; comprehensive details of each initiative can be found in the appendicies.
Social Return on Investment (SROI)
To evaluate not only the quantitative but also the qualitative and economic impacts of our community contribution investments, we have adopted the SROI analysis method. This approach allows us to calculate the economic value of the benefits our social projects provide to society. Through the SROI approach, we aim to guide our investment decisions in a data-driven and strategic manner.
In this context, we applied the SROI (Social Return on Investment) methodology in 2024 to assess the impact of our Womentum program, which was launched to support women’s career development and participation in the workforce. As a result of this analysis, it was calculated that every TL 1 investment returns to society as a social benefit worth TL 17.37. This ratio indicates that the program not only provides individual gains but also aligns closely with gender equality, economic participation, and sustainable development goals.
Within the program, women participants were supported through mentorship, workshops, and online training, achieving significant gains in areas such as confidence development, professional skills, sustainability knowledge, and gender awareness. Additionally, the program contributed to increasing women representation in sectors like engineering and energy, where women’s presence is typically low, and established a network that strengthens solidarity among women.
We will continue to integrate the SROI approach into our other social investment projects in the coming period, systematically measuring and managing social impact. Through this, we aim to make our community contributions more transparent, sustainable, and measurable.
Social Impact Analysis and Future Commitments
At Enerjisa Üretim, to contribute to sustainable development goals, we have implemented social projects in various areas such as education, regional development, gender equality, economic empowerment and livelihoods, health and social welfare, culture, and environment. In our social impact analysis conducted to measure the effects of these projects, we analyzed measurable data on the number of people affected, budget, sustainability level, and the economic, social, and environmental contributions provided. We evaluated the projects based on criteria such as alignment with SDGs, long-term impact, and replicability, clearly demonstrating their contributions to societal transformation.
In the upcoming period, we will continue to develop programs supporting women entrepreneurs, increase green energy and carbon-neutral projects, and expand initiatives focused on ensuring equal opportunities in education.
Detailed information on the projects implemented as part of Enerjisa Üretim’s social responsibility activities in renewable energy investment regions throughout 2024, within our sustainability structure and special working groups, is provided in the Appendices section.
Human Rights and Social Responsibility Principles
We place respect for human rights, ethical business practices, and social responsibility at the core of all our activities. As a signatory of the United Nations Global Compact, we maintain our commitment to full compliance with global standards in human rights, labor standards, environment, and anti-corruption. In this context, we manage our business processes fairly, inclusively, and responsibly, adopting an approach based on the principle of equality.
In line with our human rights commitment, we prioritize protecting the fundamental rights of all stakeholders in our value chain, from our employees to our business partners, integrating this approach into our policies and management systems. We systematically apply situational review processes throughout the value chain, develop a Human Rights Risk Inventory, nd regularly report current situation analyses to the Sustainability Management Committee and Ethics Board.
Our policy approach encompasses a wide range of rights-related commitments, including the promotion of freedom of expression, protection of personal data and privacy, and combating human rights violations such as child labor and forced labor. The human rights governance processes we have implemented at the corporate level are structured based on a risk-based approach and are designed to be integrated with our Risk Management, Occupational Health and Safety , Sustainability, and Social Responsibility processes. These processes are established to serve as a fundamental component of our overall management system.
In 2024, we updated our policies and procedures within the scope of gender equality and the fight against sexual violence and discrimination, enhancing human rights awareness among our stakeholders. Operating across a broad geography with varying human rights risks makes it critical that all our stakeholders uphold these rights. In 2024 we did not encounter any legal or criminal proceedings related to human rights cases.
We are fully committed to respecting human rights in our interactions with employees, suppliers, business partners, and all stakeholders. This approach is shaped by the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights. In line with this commitment, and while pledging full compliance with the highest ethical standards and legal frameworks, we actively uphold the following key commitments:
In fulfilling all these commitments, we act in accordance with the following international standards and principles: